Imagine standing on a vast, silent plain, stretching as far as the eye can see. The ground beneath your feet feels solid, unyielding, a comforting foundation for all that exists above. But what lies beneath this seemingly stable surface? Beneath the familiar landscapes, the bustling cities, the churning oceans, lies a world of unimaginable pressure, scorching heat, and secrets waiting to be revealed. This is the Earth’s interior, a realm that we can’t directly access but whose intricate properties shape our world in ways both subtle and profound.

Image: www.youtube.com
Understanding the Earth’s interior is not just an academic pursuit. It helps us comprehend the very processes that drive our planet, from the formation of mountains to the ebb and flow of continents, from the magnetic field that shields us from solar radiation to the earthquakes and volcanoes that remind us of the dynamic forces at play deep within. We can’t simply drill into the Earth’s core, but through a combination of insightful observation, ingenious experimentation, and meticulous analysis, scientists have been able to infer the properties of this hidden realm with remarkable accuracy.
Peering into the Earth’s Depths: The Tools of Inference
Our knowledge of the Earth’s interior is built on a foundation of indirect evidence. Like detectives piecing together a puzzle, scientists have developed various tools and techniques to glean clues from the surface and decipher the secrets hidden beneath.
1. Seismic Waves: The Earth’s Inner Symphony
One of the most powerful tools in our arsenal is the study of seismic waves, the vibrations that travel through the Earth’s interior, generated by earthquakes or controlled explosions. These waves behave differently depending on the material they pass through. Some waves are faster through solid rock than liquid, while others can only travel through solid material. By carefully analyzing the arrival times and wave patterns recorded by seismometers, scientists can map out the different layers of the Earth, just like a doctor uses ultrasound to visualize the human body.
Imagine a symphony, each instrument playing a unique melody. Just as the conductor can discern the different instruments by their distinct sounds, seismologists can identify different layers of the Earth through the unique “sounds” of the seismic waves. These waves provide insights into the composition, density, and state of matter within the Earth, revealing a hidden world of immense complexity.
2. Gravity: A Subtle but Telling Clue
The Earth’s gravity isn’t uniform across the globe. It is slightly stronger in some regions and weaker in others. This variation in gravity is influenced by the density of the underlying rocks. Areas with denser rock, like those containing heavy metals, have higher gravity readings, while areas with lighter rock have weaker gravity. This subtle variation in gravity gives us valuable clues about the distribution of different materials within the Earth.
Imagine placing a bowling ball on a trampoline. It will deform the trampoline, creating a dip around the bowling ball. Similarly, denser regions within the Earth pull on the surrounding rock, causing a slight distortion in the shape of the Earth. By measuring these deviations from the expected shape, scientists can infer the presence of denser materials, such as metallic cores, deep within the Earth.
3. Magnetic Field: The Earth’s Protective Shield
The Earth acts like a giant magnet, with a magnetic field extending far beyond the planet’s surface. This field serves as a protective shield, deflecting harmful solar radiation and protecting life on Earth. The source of this magnetic field lies deep within the Earth, generated by the movement of molten iron in the outer core.
Think of a spinning coin, generating a tiny magnetic field. Now imagine a massive ball of molten iron spinning within the Earth, creating a much stronger magnetic field. By analyzing the Earth’s magnetic field, its intensity and direction at different locations, scientists can gain insights into the dynamics of the outer core, its composition, and the processes that drive its movement.
4. Meteorites: Messenger from the Cosmos
While meteorites may seem like visitors from distant space, they also hold valuable clues about the Earth’s formation and the composition of its interior. Some meteorites are thought to originate from the core of ancient planets, offering a glimpse into the building blocks of our own planet. These extraterrestrial visitors provide insights into the composition of the early Earth, and the materials that formed its core, mantle, and crust.
Layers of Mystery: Unveiling the Earth’s Structure
Armed with these tools, scientists have pieced together a remarkable picture of the Earth’s interior, revealing a series of distinct layers, each with its unique properties and playing a crucial role in shaping the planet we know.
1. The Crust: The World We Know
The outermost layer of the Earth is the thin, brittle crust, like the skin of an apple. It’s composed primarily of igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks, and is divided into two parts: the oceanic crust, thinner and denser, found beneath the oceans, and the continental crust, thicker and lighter, forming the landmasses we inhabit. The crust is constantly evolving, with the formation of new crust at mid-ocean ridges and the destruction of old crust at subduction zones, where one plate dives beneath another.
Imagine a mosaic, with different tiles representing different rock formations. The crust is like this mosaic, a collection of rock types that have been shaped and transformed over millions of years. These rock formations hold stories of the Earth’s history, from ancient volcanoes to the remnants of prehistoric life.
2. The Mantle: A Dynamic Layer of Rock
Beneath the crust lies the mantle, a vast layer of solid rock, but not in the way we usually think of solid. The immense pressure and heat in the mantle cause the rock to behave like a viscous fluid, able to flow slowly over geological time scales. This slow flow, powered by heat from the Earth’s core, drives plate tectonics, the movement of the Earth’s crust that shapes continents, creates mountains, and triggers earthquakes and volcanoes.
Imagine a pot of honey on a hot stove. The honey at the bottom of the pot heats up and becomes less viscous, allowing it to flow more readily. The mantle is like this pot of honey, with hotter, less viscous rock rising to the surface, while cooler, denser rock sinks. This constant circulation of rock is what drives the movement of the plates that make up the Earth’s surface.
3. The Outer Core: A Sea of Molten Iron
Beneath the mantle lies the outer core, a fluid layer of molten iron and nickel. This molten iron is constantly moving, driven by the Earth’s rotation and convection currents, generating the Earth’s magnetic field. The magnetic field acts as a shield, deflecting harmful radiation from the sun and protecting life on Earth.
Imagine a giant pot of molten metal, with currents constantly swirling and churning. This churning creates electrical currents, which in turn generate a magnetic field. The Earth’s outer core is like this gigantic, churning pot of molten iron, producing the magnetic field that protects us from the sun’s harmful radiation.
4. The Inner Core: A Solid Ball of Iron
At the Earth’s center lies a solid ball of iron and nickel, known as the inner core. The immense pressure on the inner core is so strong, it actually prevents the iron from melting, even though temperatures here are incredibly hot. This solid core, like a super-heated ball of iron, plays a significant role in generating the Earth’s magnetic field.
Imagine a steel ball, compressed in a vice. The immense pressure in the vice prevents the steel from melting, even though it is very hot. The inner core is similar, with the immense pressure of the surrounding layers preventing the iron from melting, despite the incredibly high temperatures.
Unlocking the Mysteries: The Future of Inferring Earth’s Interior
While immense progress has been made in deciphering the secrets of the Earth’s interior, there are still many unanswered questions. Scientists are constantly refining their techniques and developing new technologies to improve our understanding of this hidden world.
1. Advanced Seismic Imaging: Scientists are developing new techniques for analyzing seismic waves, using sophisticated algorithms and artificial intelligence to improve the accuracy of deep-earth imaging.
2. Geochemistry and Mineralogy: New laboratory experiments are being conducted to study the behavior of minerals under extreme pressure and temperature, providing insights into the composition and properties of the Earth’s mantle and core.
3. Space-Based Observations: Satellites equipped with advanced sensors are being used to measure the Earth’s gravity field with unprecedented precision, revealing subtle variations that can provide clues about the composition and structure of the Earth’s interior.
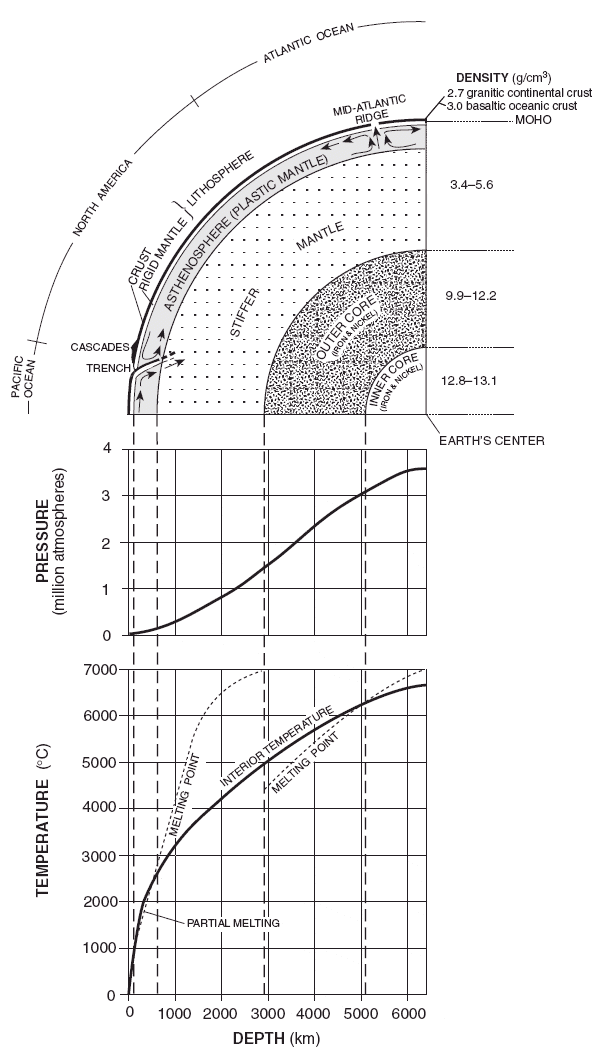
Image: cl.castlelearning.com
Inferred Properties Of Earth’S Interior
In Conclusion: The Earth’s Interior – A Constant Source of Wonder
The Earth’s interior, a realm hidden deep beneath our feet, is a testament to the extraordinary forces that shape our planet. Through a combination of ingenious observation, meticulous analysis, and tireless research, scientists have made significant strides in understanding this hidden world. The insights we gain from exploring the Earth’s interior have profound implications for our understanding of the planet’s evolution, its dynamic processes, and the resources it holds. The quest to unlock the secrets of the Earth’s interior is a fascinating journey that continues to inspire and captivate generations of scientists, reminding us that even in the most familiar places, there is always more to discover.



/GettyImages-173599369-58ad68f83df78c345b829dfc.jpg?w=740&resize=740,414&ssl=1)


