Imagine a patient lying in a hospital bed, feeling weak and feverish, their body battling an unknown enemy. The doctor’s face is etched with concern, and the question hangs heavy in the air: “Could it be sepsis?” This life-threatening condition, a dangerous response to infection, could spread rapidly, putting the patient’s life at risk. But the only way to know for sure is through a simple, yet vital, procedure: drawing blood cultures.

Image: mungfali.com
This seemingly routine medical practice holds the power to identify and conquer the invading microbes, offering a lifeline for countless patients. Drawing blood cultures is a critical skill for healthcare professionals, requiring meticulous technique, unwavering attention to detail, and a deep understanding of the intricate world of microorganisms.
Understanding the Significance of Blood Cultures
Blood cultures are like tiny windows into the human body, giving healthcare professionals a glimpse into the often-invisible battleground of infection. They reveal the presence of bacteria, fungi, or even viruses lurking within our bloodstreams, allowing physicians to diagnose and treat infections effectively.
The Journey of a Blood Culture
Every blood culture begins with a simple blood draw, employing sterile techniques to prevent contamination. As the blood enters the culture bottle, it encounters a nutrient-rich environment, welcoming any microorganisms present. It’s a journey of incubation, where those tiny invaders are given a chance to multiply and reveal their presence.
Decoding the Results
The incubation period, a waiting game of sorts, allows for the amplification of any microorganisms present. Once they have multiplied sufficiently, the blood culture is examined under a microscope, revealing the culprits behind the infection. Identifying the specific type of microbe is crucial, as this information dictates the choice of antibiotics, ensuring a targeted and effective treatment plan.
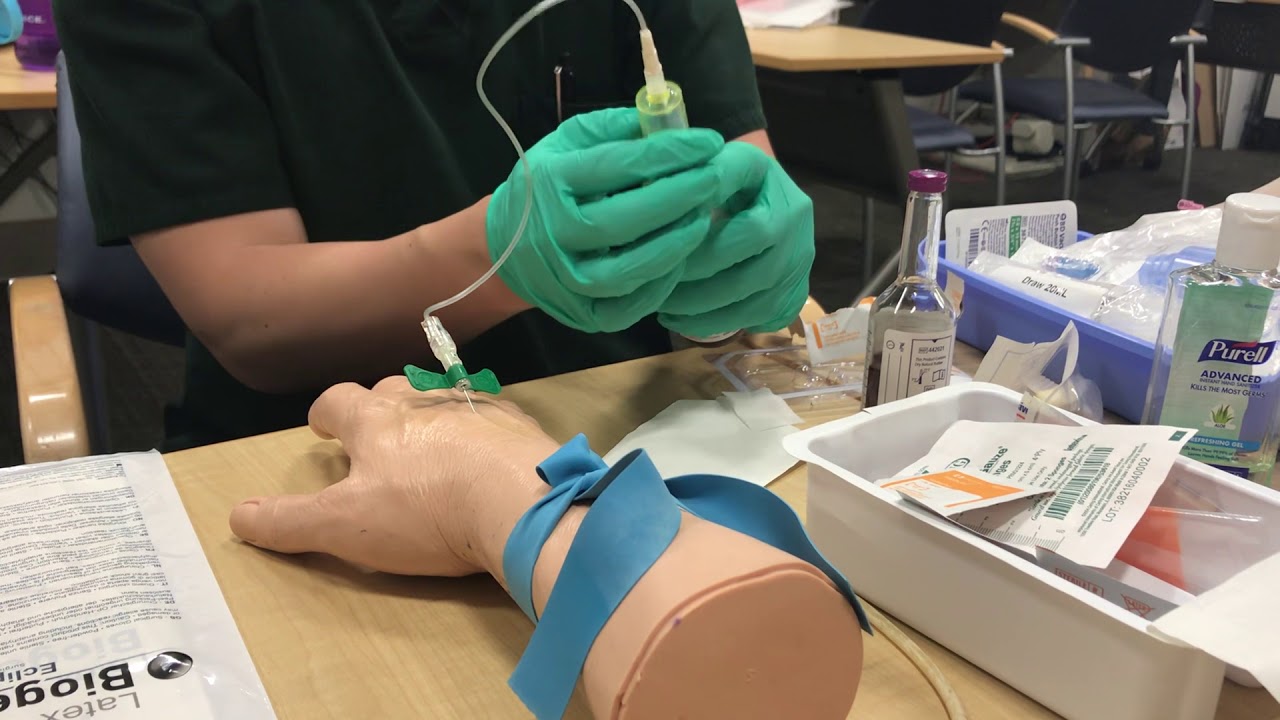
Image: bornmodernbaby.com
From Theory to Practice: A Step-by-Step Guide
Drawing blood cultures may seem straightforward, but the meticulousness involved makes it an art form. Here’s a detailed guide to ensure accurate and safe blood culture collection:
1. Gather Your Supplies
Before you begin, ensure you have all the necessary supplies within reach.
- Sterile culture bottles: These are specially designed to contain the blood sample and provide the optimal environment for microbial growth. Different bottles are available for aerobic, anaerobic, and fungal cultures.
- Sterile syringes: Use syringes appropriate for the volume of blood required for each culture bottle.
- Alcohol swabs: These are used to disinfect the patient’s skin, reducing the risk of contamination.
- Tourniquet: This helps make the veins more prominent, facilitating easier blood draws.
- Gloves: Wearing gloves ensures personal safety and prevents contamination of the sample.
- Labels: Clearly label each culture bottle with the patient’s name, date, time, and the type of culture collected.
2. Prepare the Patient
Comfort and communication are crucial for a smooth procedure.
- Explain the procedure: Clearly explain the process to the patient, alleviating any anxiety and ensuring their cooperation.
- Secure a comfortable position: Ensure the patient is comfortable and relaxed, allowing for easy vein access.
- Locate an appropriate vein: Choose a vein suitable for the required blood volume, ensuring it is visible and accessible.
3. Perform the Blood Draw
This is where the art of drawing blood cultures comes to life.
- Cleanse the venipuncture site: Use an alcohol swab to thoroughly clean the chosen area, ensuring it is completely dry before proceeding.
- Apply the tourniquet: Tighten the tourniquet above the chosen venipuncture site to distend the vein and make it easier to access.
- Prepare the syringe: Use a sterile syringe and carefully draw air into it, equal to the volume of blood required.
- Insert the needle: Insert the needle into the selected vein at a suitable angle.
- Obtain the blood sample: Draw the required amount of blood into the syringe.
- Draw blood culture bottles: Immediately transfer the blood into each culture bottle, ensuring the appropriate volume is drawn for each.
- Remove the needle and apply pressure: Gently remove the needle and apply pressure to the venipuncture site using a sterile gauze pad.
4. Post-Procedure Care
The final step in this delicate process is crucial for patient comfort and safety.
- Monitor the patient: Observe the patient closely for any signs of discomfort, bleeding, or bruising.
- Properly label and transport: Ensure all culture bottles are clearly labeled and transport them to the laboratory as soon as possible to ensure optimal results.
Expert Insights and Actionable Tips
Drawing blood cultures is a critical skill requiring ongoing training and continuous improvement. Experts emphasize the following factors:
- Sterility is paramount: Maintaining a sterile environment throughout the procedure is crucial to prevent contamination and ensure accurate results.
- Proper blood volume matters: Ensuring the correct volume of blood is drawn for each culture bottle is vital for optimal growth of microorganisms.
- Prompt delivery: Delivering the blood cultures to the laboratory promptly allows for timely processing and accurate identification of potential infections.
How To Draw Blood Cultures
Conclusion
Drawing blood cultures is a critical tool in the fight against infection. By understanding the procedure, adhering to sterile techniques, and staying vigilant, healthcare professionals can contribute to better diagnoses and more effective treatments. As we continue to learn more about the complex world of microbes, the practice of drawing blood cultures will continue to play a vital role in ensuring the health and well-being of countless patients.
Embrace this skill with confidence, for the knowledge you gain and the lives you touch will make all the difference.



/GettyImages-173599369-58ad68f83df78c345b829dfc.jpg?w=740&resize=740,414&ssl=1)


