Have you ever woken up with a strange feeling in your ear, a sense of fullness or even a dull ache? Perhaps you notice a yellow or greenish discharge, sometimes accompanied by a foul odor. While occasional earwax buildup is a normal occurrence, persistent ear discharge, known medically as otopyorrhea, could signal a more serious underlying issue. This article delves into the world of otopyorrhea, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. Understanding this condition can empower you to seek timely medical attention and navigate the path to a healthy ear.

Image: www.pinterest.co.uk
Otopyorrhea, simply put, is the flow of pus or other discharge from the ear. It can be a disconcerting experience, often accompanied by pain, itchiness, and hearing loss. This condition can arise from various factors, ranging from simple ear infections to more complex conditions like chronic otitis media and even tumors. Understanding the potential causes of otopyorrhea is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment path and ensuring optimal ear health.
Understanding the Root Causes of Otopyorrhea
The ear, a complex and delicate organ, is susceptible to infections and inflammation. Otopyorrhea often arises as a symptom of these underlying issues. Here’s a breakdown of the most common causes of ear discharge:
1. Otitis Media: An Inner Ear Infection
Otitis media, an infection of the middle ear, is a primary culprit behind otopyorrhea. This condition can occur at any age, but it’s particularly prevalent in children due to their shorter and more horizontal Eustachian tubes, which connect the middle ear to the back of the throat. When these tubes become blocked, fluids can get trapped in the middle ear, creating a fertile ground for bacterial or viral infections.
The symptoms of otitis media can range from mild to severe. They may include:
- Ear pain
- Fever
- Irritability in infants and toddlers
- Fluid draining from the ear
- Hearing loss
2. External Otitis: An Infection of the Outer Ear
External otitis, also known as swimmer’s ear, is an infection of the outer ear canal. It’s frequently caused by water trapped in the ear after swimming, particularly in warm, humid environments. This moist environment promotes the growth of bacteria and fungi, leading to inflammation and discharge.
The characteristic symptoms of external otitis include:
- Pain, especially when pulling on the earlobe
- Itching in the ear canal
- Swelling and redness around the ear opening
- Discharge from the ear
- Hearing loss
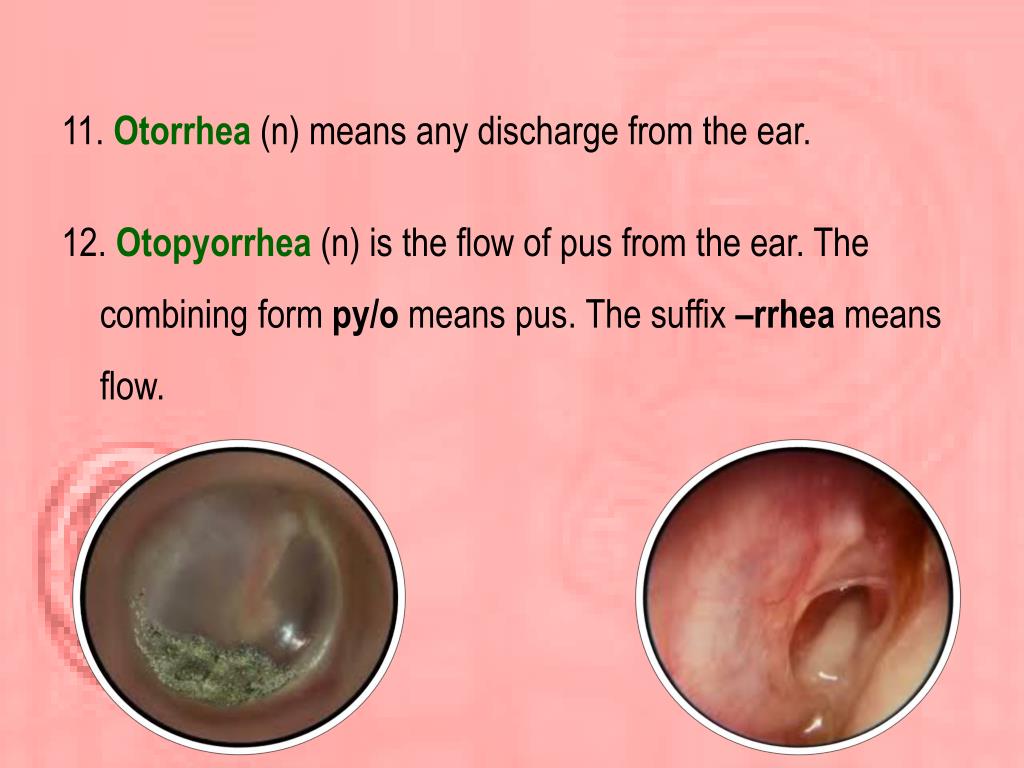
Image: www.slideserve.com
3. Chronic Otitis Media: Persistent Middle Ear Inflammation
Chronic otitis media is a persistent infection of the middle ear that fails to resolve with conventional antibiotic treatment. It can lead to persistent ear discharge, often tinged with blood or pus, and can significantly impact hearing. This condition can be caused by various factors, including:
- Eustachian tube dysfunction: This condition prevents proper drainage of fluid from the middle ear, creating an environment conducive to infection.
- Chronic nasal allergies: Allergies can inflame the Eustachian tube and promote fluid buildup in the middle ear, leading to infection.
- Structural abnormalities: Some people are born with anatomical variations that make them more prone to chronic otitis media.
4. Cholesteatoma: A Growths in the Middle Ear
Cholesteatoma, a noncancerous skin growth in the middle ear, can lead to otopyorrhea. This growth can occur due to repeated ear infections or other factors. It can erode bones in the middle ear and damage the eardrum, leading to hearing loss and persistent discharge.
5. Other Causes: Beyond Infections
Otopyorrhea can also be caused by factors unrelated to infection. These include:
- Foreign objects in the ear: Small objects lodged in the ear canal can cause irritation and discharge.
- Ear injuries: Trauma to the ear can lead to tears in the eardrum, resulting in discharge.
- Tumors: While rare, tumors in or around the ear can cause otopyorrhea.
Diagnosing the Cause: Unveiling the Puzzle
Determining the underlying cause of otopyorrhea is essential for effective management. A thorough evaluation by an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist is crucial. The physician will conduct a comprehensive examination, including:
1. Medical History: Unraveling the Past
The ENT doctor will gather detailed information about your medical history, including prior ear infections, allergies, and any recent trauma to your ear. This information helps understand the potential contributing factors to otopyorrhea.
2. Physical Examination: Inspecting the Ear
A thorough examination of your ear canal and eardrum is essential. The doctor will use an otoscope, a handheld instrument with a light and magnifying lens, to visualize the structures of your ear. This examination helps identify any abnormalities, such as inflammation, fluid buildup, or foreign objects.
3. Audiometry: Assessing Hearing Loss
An audiometry test measures your hearing ability. This test helps determine the extent of hearing loss, if any, associated with otopyorrhea. By analyzing your hearing threshold at different frequencies, the doctor can get a better understanding of the underlying cause of otopyorrhea.
4. Imaging Studies: A Deeper Look
In some cases, the ENT doctor may recommend imaging studies to obtain a more detailed view of the ear structures. Common imaging techniques include:
- CT scan: This scan provides cross-sectional images of the ear bones and surrounding structures, enabling the doctor to visualize potential abnormalities.
- MRI scan: This technique provides detailed images of soft tissues, which are useful in identifying tumors or other abnormalities.
Navigating Treatment Options: A Path to Recovery
The treatment for otopyorrhea depends on the underlying cause. Once the culprit is identified, the ENT doctor will recommend the most appropriate course of action.
1. Medical Treatment: Targeting the Cause
For infections, antibiotics are often prescribed. The specific type of antibiotic will depend on the type of bacteria causing the infection. In some cases, ear drops containing antibiotics and corticosteroids may be used to reduce inflammation and infection.
For chronic otitis media, treatment may involve:
- Antibiotics: Long-term antibiotic treatment can help control the infection.
- Tympanostomy tubes: These small tubes are inserted into the eardrum to help drain fluid from the middle ear and prevent infection.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to improve drainage or address structural abnormalities that contribute to chronic otitis media.
2. Home Remedies: Providing Relief
While home remedies cannot cure otopyorrhea, they can provide temporary relief from symptoms and support the healing process. These include:
- Warm compresses: Apply a warm compress to the affected area for 10-15 minutes several times a day to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers: Medications such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help relieve pain.
- Ear drops: Certain over-the-counter ear drops can help soften earwax and promote drainage, but consult your doctor before using them.
3. Preventing Recurrences: Taking Charge of Your Ear Health
Preventing otopyorrhea from recurring is key to long-term ear health. Here are some preventive measures:
- Proper hygiene: Wash your hands frequently, especially before touching your ears. Avoid sharing personal items like towels or ear buds.
- Avoid excess water in your ears: When swimming, use earplugs or keep your head above water. After swimming, gently dry your ears with a towel or a hairdryer on the lowest setting.
- Treat ear infections promptly: See your doctor at the first sign of an ear infection, as early treatment can help prevent complications.
- Manage allergies: Control allergies to minimize inflammation in the nasal passages, which can contribute to ear infections.
Otopyorrhea
Conclusion: Taking Action for Your Ear Health
Otopyorrhea, while often disconcerting, is treatable with proper diagnosis and management. Understanding the underlying causes of ear discharge empowers you to seek timely medical attention, enhancing the prospect of successful treatment. Whether it’s an infection, chronic inflammation, or an anatomical variation, your ENT doctor is equipped to diagnose the cause and develop a personalized treatment plan. Remember, persistent ear discharge shouldn’t be ignored. By taking action and working closely with your healthcare provider, you can put your ear health back on track and enjoy the gift of clear hearing.



/GettyImages-173599369-58ad68f83df78c345b829dfc.jpg?w=740&resize=740,414&ssl=1)


