Ever wondered how to translate the scorching 1013°F, a temperature often associated with intense heat, into the more familiar Celsius scale? The conversion from Fahrenheit to Celsius isn’t just about swapping scales; it’s about understanding the fundamental differences in how these two systems perceive temperature and how that understanding impacts our daily lives.

Image: theatrecouple12.bitbucket.io
This article delves into the conversion process, exploring the history and significance of Fahrenheit and Celsius, and showcasing the relevance of the conversion in diverse fields, from everyday cooking to scientific research.
Understanding the Conversion
The conversion from Fahrenheit (°F) to Celsius (°C) involves a straightforward formula:
°C = (°F – 32) × 5/9
In essence, we subtract 32 from the Fahrenheit temperature, then multiply the result by 5/9. This mathematical transformation accurately translates the temperature value between the two scales.
The History Behind Fahrenheit and Celsius
To grasp the conversion’s significance, we must delve into the history of the two scales. The Fahrenheit scale, named after German physicist Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit, was introduced in 1724. Fahrenheit initially set the zero point based on the freezing point of a salt-water solution. Later, he defined 32°F as the freezing point of water and 212°F as the boiling point of water at sea level.
The Celsius scale, named after Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius, was developed in 1742. Originally, Celsius set 0°C as the boiling point of water and 100°C as the freezing point. However, his scale was later reversed, with 0°C representing the freezing point of water and 100°C representing the boiling point – a system we use today.
Why Convert Fahrenheit to Celsius?
The conversion from Fahrenheit to Celsius is vital for various reasons, including:
- International Communication: Most of the world uses the Celsius scale, making conversion necessary for clear and accurate communication in various fields, including science, trade, and travel.
- Scientific Research: Scientific research often uses Celsius, ensuring uniformity and consistency in measurements and data analysis across different laboratories globally.
- Global Climate Change: Discussions on climate change and global warming rely on Celsius measurements, fostering a shared understanding of climate data and trends.
- Cooking and Baking: Many recipes use Celsius measurements, requiring conversion for accurate results.
- Technological Applications: Devices like ovens, thermometers, and weather reports often provide measurements in Celsius, requiring conversion for better understanding.
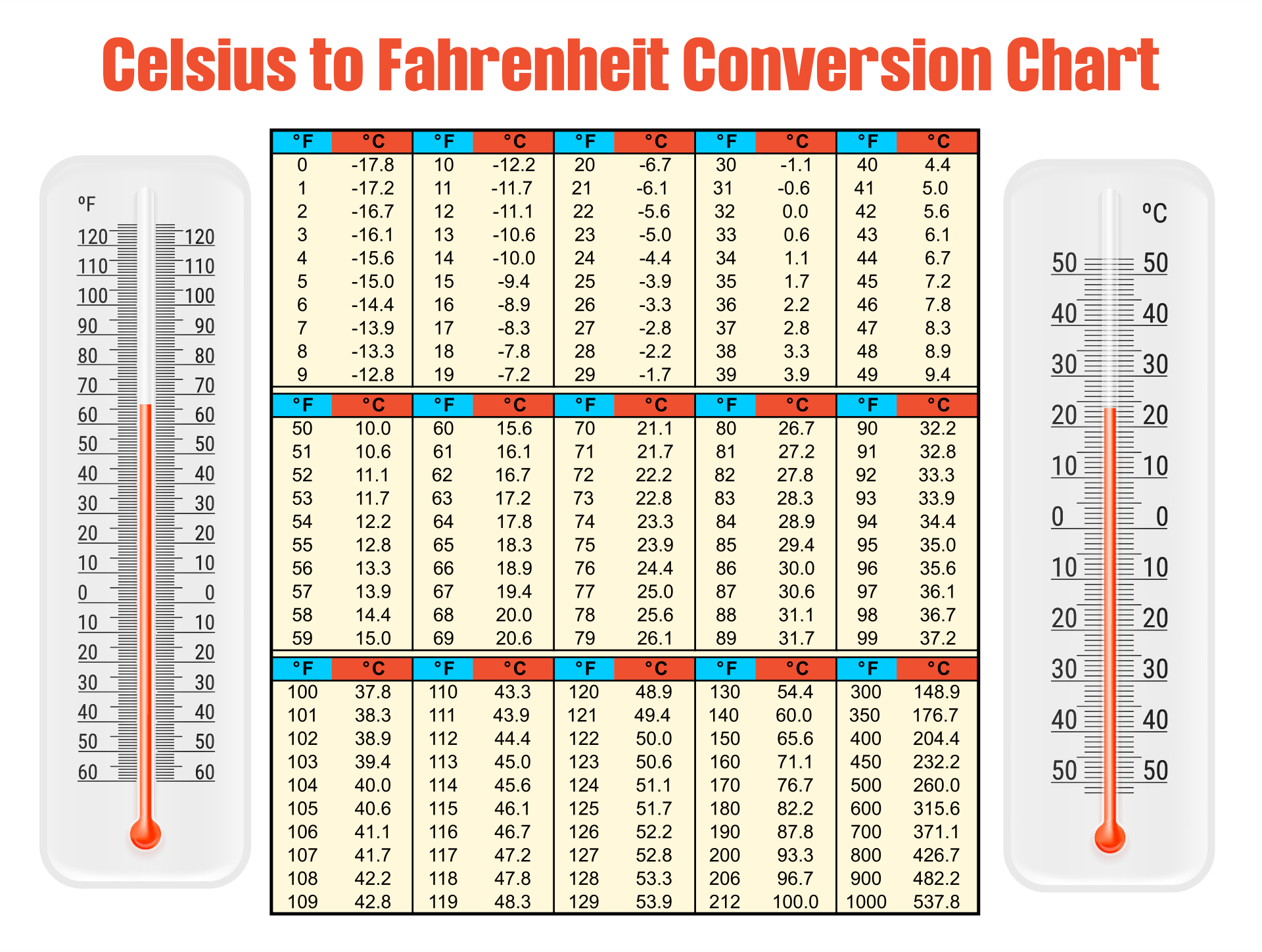
Image: www.tpsearchtool.com
Real-World Applications of the Conversion
Consider the following examples to visualize the everyday relevance of converting Fahrenheit to Celsius:
- Weather Reports: While the United States uses Fahrenheit for weather, most other countries rely on Celsius. If you are traveling to a country that uses Celsius, you will need to convert the temperature to understand the weather conditions.
- Medical Thermometers: Many medical thermometers provide measurements in Celsius, requiring conversion to Fahrenheit for those accustomed to the US system.
- Baking and Cooking: Cooking temperatures are usually expressed in Celsius in most countries, necessitating a conversion for following recipes in other systems.
- Scientific Experiments: Scientists worldwide use Celsius in their research, making it essential to convert Fahrenheit measurements for consistency and communication within the scientific community.
Beyond the Conversion: The Future of Temperature Scales
While Fahrenheit and Celsius remain the dominant scales, discussions around alternative systems, such as the Kelvin scale, are gaining traction. The Kelvin scale, rooted in absolute zero, is crucial in fields involving high temperatures and fundamental physics.
The future of temperature scales will likely witness a blend of traditional systems and new developments, driven by factors like international collaboration, advancements in scientific research, and the need for a unifying and universal approach.
1013 F To C
Conclusion
The conversion from 1013°F to Celsius, equivalent to a scorching 545°C, highlights the need for understanding and applying different temperature scales. From everyday activities like cooking to crucial research in various fields, the ability to translate measurements across systems is vital for accurate communication and scientific progress. By embracing both Fahrenheit and Celsius, alongside potential future developments, we can navigate the complex world of temperature measurements with greater clarity and efficiency.



/GettyImages-173599369-58ad68f83df78c345b829dfc.jpg?w=740&resize=740,414&ssl=1)


