Have you ever wondered about the invisible forces that govern the behavior of molecules? It’s a fascinating world where even the tiniest particles play a critical role in our everyday lives. Take sulfur dioxide (SO2), for instance. This colorless gas with a pungent odor is a significant player in air pollution and contributes to acid rain. But beyond its environmental impact, SO2 holds a secret: it’s a polar molecule, a fact that unravels a fascinating story about the intricate arrangement of atoms and their impact on chemical behavior.
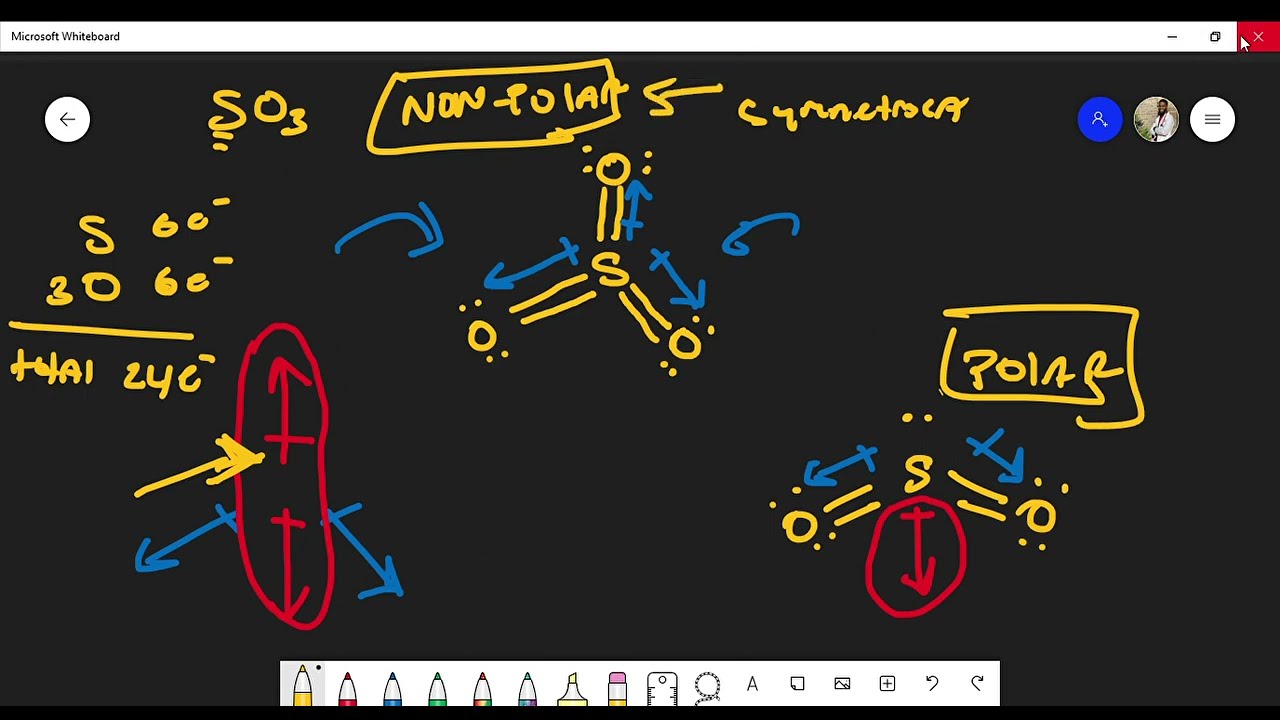
Image: www.youtube.com
In this comprehensive exploration, we’ll delve into the world of SO2, unraveling why it’s a polar molecule and understanding what that means for its properties and interactions. We’ll also explore the broader significance of polarity in chemistry and its relevance in understanding the behavior of various molecules. By understanding these concepts, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate dance of atoms that shapes our world.
The Building Blocks of Polarity: Understanding Molecular Geometry
To understand why SO2 is a polar molecule, we need to take a journey into the realm of molecular geometry. Imagine a molecule as a miniature sculpture where atoms are connected by chemical bonds. The way these atoms are arranged in space – their geometry – significantly influences the molecule’s properties, including its polarity.
The central atom in SO2, sulfur, forms two double bonds with oxygen atoms. In other words, each oxygen atom shares two electrons with sulfur, resulting in a strong connection. The arrangement of these bonds dictates the shape of the molecule.
Sulfur dioxide adopts a bent or V-shaped molecular geometry. This arrangement arises from the fact that the sulfur atom has two lone pairs of electrons. These lone pairs, located on the sulfur atom, repel the double bonds with the oxygen atoms, causing them to bend away from each other.
The Essence of Polarity: Uneven Distribution of Charges
Imagine two magnets, one with a positive pole and the other with a negative pole. When you bring them close, they attract. Now, consider a molecule as having its own magnetic poles, albeit on a much smaller scale. These poles arise from the unequal distribution of electron density.
While the sulfur-oxygen bonds in SO2 are covalent, meaning they share electrons, the sharing isn’t perfectly equal. Oxygen is more electronegative than sulfur, meaning it attracts electrons more strongly. This difference in electronegativity creates a slight negative charge on the oxygen atoms and a slight positive charge on the sulfur atom. Since the oxygen atoms are positioned on either side of the sulfur atom, and the lone pairs of electrons on the sulfur atom cause the molecule to bend, the uneven distribution of charge creates a dipole moment.
The Consequences of Polarity: The Influence on Molecular Behavior
The polarity of SO2 has significant consequences for its behavior and interactions.
- Solubility: Polar molecules like SO2 tend to dissolve in polar solvents such as water. This occurs because the positive end of a water molecule can interact with the negative end of SO2, while the negative end of a water molecule can interact with the positive end of SO2. This mutual attraction facilitates dissolving.
- Intermolecular forces: The dipole moment of SO2 leads to dipole-dipole interactions, which are stronger than the London dispersion forces found in nonpolar molecules. These forces influence the melting point and boiling point of SO2, making it a gas at room temperature.
- Reactivity: The polarity of SO2 influences its reactivity with other molecules. It can readily react with water to form sulfurous acid (H2SO3), a key component of acid rain.

Image: sciencetrends.com
The Wider World of Polar Molecules: A Journey into Chemistry
Understanding the polarity of SO2 is not just a theoretical exercise. It opens doors to appreciating the intricate world of chemical interactions. Polar molecules play crucial roles in biological systems, influencing how proteins fold, how enzymes catalyze reactions, and how cell membranes function.
Polarity also plays a significant role in the properties of materials. For instance, the polarity of certain polymers influences their behavior and applications. The properties of plastics, paints, and even detergents are heavily influenced by the polarity of the molecules they consist of.
Beyond the Textbook: The Role of SO2 in the Real World
The story of SO2 doesn’t end with its polar nature. It’s a crucial player in atmospheric chemistry, influencing climate change and impacting our air quality. SO2 is released into the atmosphere primarily through the burning of fossil fuels and industrial processes.
When SO2 combines with moisture in the atmosphere, it forms sulfuric acid (H2SO4), which contributes to acid rain. Acid rain can damage ecosystems, harming forests, aquatic life, and buildings.
The Importance of Understanding Polarity: A Call to Action
Understanding polarity is crucial to comprehending the behavior of chemical substances and their impact on our environment. It allows us to make informed decisions about how we interact with and utilize these substances.
As responsible citizens, we can contribute to reducing SO2 emissions by supporting renewable energy sources, choosing energy-efficient products, and advocating for sustainable practices. By understanding the science behind these issues, we can become more informed advocates for a healthier planet.
Is So2 Polar Or Nonpolar
Conclusion: Navigating the Molecular World
We’ve journeyed through the fascinating world of sulfur dioxide, discovering why it’s a polar molecule and how its polarity influences its behavior. By understanding the basic principles of molecular geometry and polarity, we can unravel the intricate dance of molecules that governs our world.
From the fundamental properties of materials to the complex mechanisms of biological systems, polarity plays a critical role in shaping our universe. This knowledge empowers us to make informed decisions about how we engage with the world around us and work towards a more sustainable and resilient future.



/GettyImages-173599369-58ad68f83df78c345b829dfc.jpg?w=740&resize=740,414&ssl=1)


