Have you ever stopped to consider the hidden layers beneath the surface of our everyday actions? We go to work, attend school, and participate in community events—seemingly straightforward activities. However, beneath these surface-level interactions lie intricate webs of social functions, many of which are deliberate, others less so. This is where the concept of “manifest function” comes into play, a cornerstone of sociological thinking that offers a fascinating lens through which to examine the complexities of human behavior.
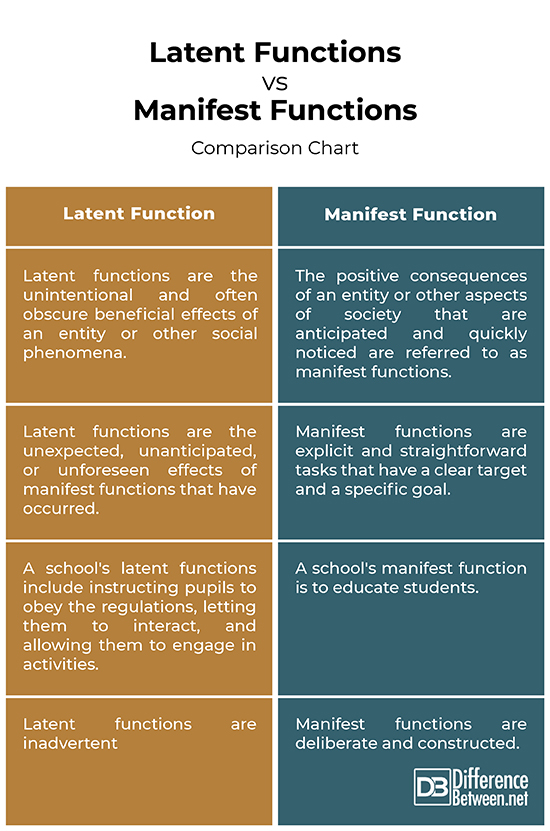
Image: www.differencebetween.net
What is manifest function in sociology? Simply put, it refers to the intended and recognized consequences of a social pattern, institution, or action. Think of it as the visible, intended outcome—the obvious reason behind why we do what we do. But delve deeper, and you’ll discover a world of unintended consequences—the hidden implications that often shape our society in unexpected ways.
Unpacking the Essence: Manifest Function Defined
To truly grasp the concept of manifest function, we need to step back and understand the broader framework of sociology. Imagine society as an intricate machine, with each part playing a vital role in its smooth operation. Sociologists, the engineers of this societal machine, seek to understand its workings, exploring the forces that drive human interaction and shape the patterns of our lives.
One of the key tools in their toolkit is the concept of “social function,” which refers to the consequences of a social pattern for the operation of society as a whole. This overarching concept then divides into two crucial aspects: manifest function and latent function.
- Manifest Function: Think of it as the “intended” or “obvious” consequence of a social action. It’s what we set out to achieve, the reason we engage in a specific behavior.
- Latent Function: This represents the less obvious, often unintended consequences of a social action. These outcomes may be positive, negative, or neutral, but they’re often overlooked or unanticipated.
Examples of Manifest Function in Action
Let’s look at some real-world examples to illustrate the concept of manifest function:
- Education: The manifest function of education is to impart knowledge and skills to students, preparing them for future employment and participation in society. We send our children to school with the clear intention of equipping them with the tools they need to thrive.
- Marriage: The manifest function of marriage is to establish a legally recognized union between two individuals, often with the goal of creating a family and sharing life’s experiences together.
- Religion: The manifest function of religion is to provide individuals with a framework for understanding the world, offering spiritual guidance, and fostering a sense of community. It provides answers to existential questions and offers a path to moral living.
- Government: The manifest function of government is to maintain order, protect citizens, and provide essential services like public healthcare, infrastructure, and education. It’s the backbone of our society, ensuring its smooth functioning and the safety of its citizens.
These examples highlight the intended, visible outcomes of these social actions. However, delve deeper, and you’ll encounter the latent functions that often go unnoticed.
Unveiling the Hidden Layers: Latent Functions of Social Actions
The concept of latent function adds a layer of complexity and intrigue to our understanding of society. These unintended consequences can be positive, negative, or even paradoxical, often shaping our world in ways we don’t anticipate.
- Education: Beyond simply imparting knowledge, education can also serve as a mechanism for social control. Schools instill specific values, norms, and behaviors, subtly shaping children’s perspectives and preparing them for their roles in society.
- Marriage: While intended as a union of love and partnership, marriage can also be a source of social status and economic advantage. It can solidify social hierarchies and reinforce existing power structures.
- Religion: Beyond providing spiritual guidance, religion can also serve as a social network, promoting community building and providing emotional support. It can also play a role in shaping cultural norms and even political movements.
- Government: While intended to serve its citizens, government can also be a tool for political manipulation and control. It can influence public opinion, shape economic policies, and even suppress dissent.

Image: keplarllp.com
The Limitations of Manifest and Latent Function
While the concepts of manifest and latent function offer a valuable framework for understanding social actions, they’re not without their limitations. Here’s why:
- Subjectivity: The distinction between manifest and latent function can be subjective. What one person perceives as an intended outcome, another might view as an unintended consequence.
- Oversimplification: The concepts tend to oversimplify complex social phenomena, reducing them to a list of functions. Social interactions are far more nuanced and interconnected.
- Ignoring Power Dynamics: The concepts don’t adequately address the power dynamics inherent in social systems. They often overlook the role of inequality, oppression, and social stratification in shaping outcomes.
Harnessing the Power of Manifest and Latent Function
Despite these limitations, the concepts of manifest and latent function offer invaluable tools for understanding our world and shaping our actions. By becoming aware of the intended and unintended consequences of our actions, we can:
- Promote Social Change: By recognizing unintended consequences, we can work to mitigate negative effects and maximize positive outcomes. For example, recognizing the potential for educational institutions to perpetuate social inequality can lead to initiatives promoting equity and access.
- Make Informed Decisions: By understanding the potential ramifications of our decisions, we can make more informed choices as individuals, organizations, and policymakers. This awareness can lead to more equitable and sustainable outcomes.
- Promote Critical Thinking: The concept of latent function encourages us to question assumptions, explore hidden motivations, and analyze social phenomena with a critical eye. This fosters critical thinking and a deeper understanding of the interconnectedness of social life.
What Is Manifest Function In Sociology
https://youtube.com/watch?v=LcluY6UsVXY
Conclusion: Unveiling the Intricacies of Social Action
The concept of manifest function is a powerful lens through which to understand the complexities of our social world. While not without its limitations, it encourages us to look beneath the surface, recognizing both the intended and unintended consequences of our actions. By embracing the critical lens of sociological thinking, we can become more informed and responsible members of society, working toward a more just and equitable future.
So, the next time you engage in a seemingly mundane social interaction, remember the unseen layers of manifest and latent function at play. The world is full of hidden intentions and unintended consequences, and understanding these nuances can empower us to shape our society in more intentional and positive ways.



/GettyImages-173599369-58ad68f83df78c345b829dfc.jpg?w=740&resize=740,414&ssl=1)


