Imagine a bustling city, teeming with people from all walks of life. Some live in opulent skyscrapers overlooking the cityscape, while others reside in modest apartments, their lives interwoven with the rhythm of the city’s pulse. This seemingly simple image encapsulates a fundamental concept: social stratification. It’s a concept that shapes our lives, influences our opportunities, and defines our social realities. But what exactly does social stratification mean?
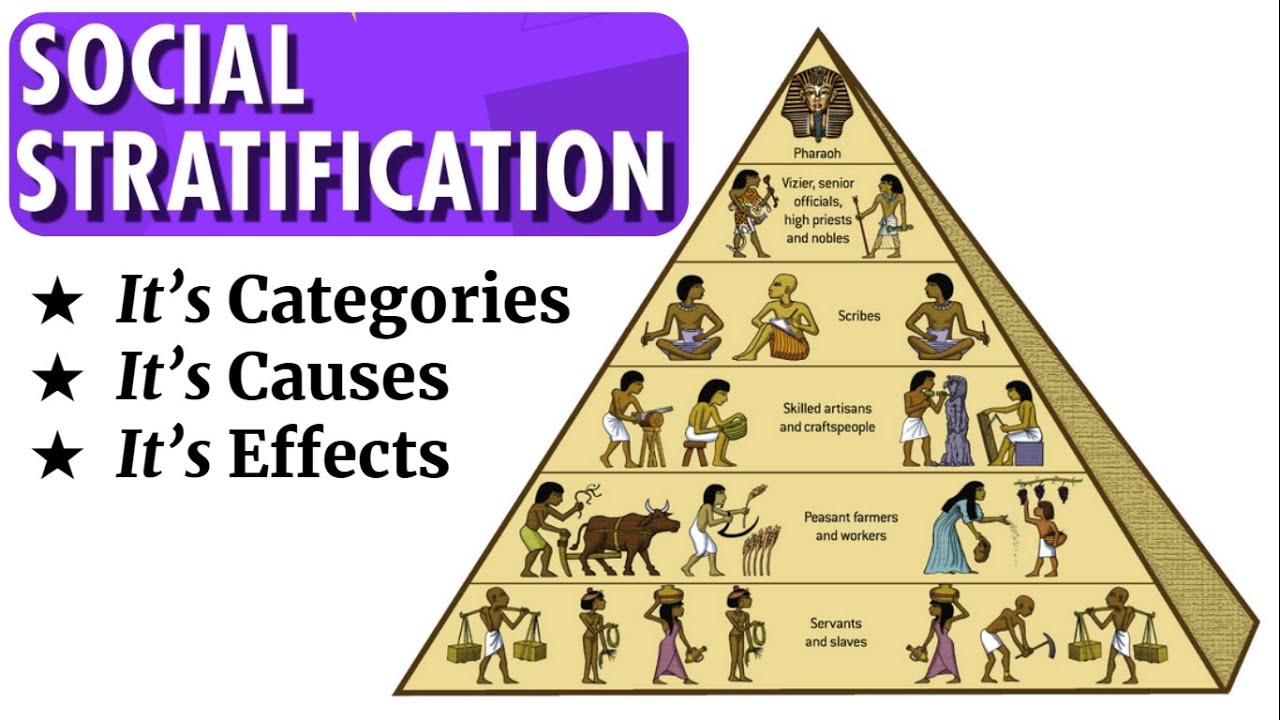
Image: socialstratificati0n.blogspot.com
In essence, social stratification refers to the hierarchical arrangement of individuals and groups in a society based on factors such as wealth, power, and prestige. It’s about understanding the inequalities that exist within a society and the systems that perpetuate those inequalities. This intricate system of social ranking, often invisible yet undeniably influential, impacts our lives in countless ways, shaping our access to education, healthcare, and even our social networks.
Exploring the Layers of Social Stratification
Social stratification is not a monolithic structure; it’s characterized by distinct layers, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. These layers are often referred to as social classes, and within each class, individuals share certain common traits, including economic status, social prestige, and political influence. To understand these layers, let’s delve into the key concepts of social stratification:
1. The Definition of Social Stratification
Social stratification is a system of inequality that is inherent within societies. It’s a way of categorizing people based on their position in the social hierarchy. This categorization happens based on various factors, including wealth, income, education, occupation, and social connections. Imagine a pyramid; at the top sits the elite, possessing the most power and resources, while those at the base have limited access to resources and often face significant social disadvantages.
2. The History of Social Stratification
Social stratification is not a modern invention; it’s a phenomenon that has existed throughout human history. In early societies, social status was often determined by factors like lineage, birthright, and kinship. As societies evolved and became more complex, new forms of stratification emerged. The development of agriculture led to the rise of landowning elites, while the Industrial Revolution created a new class of industrial workers and entrepreneurs, leading to the emergence of new forms of class consciousness.
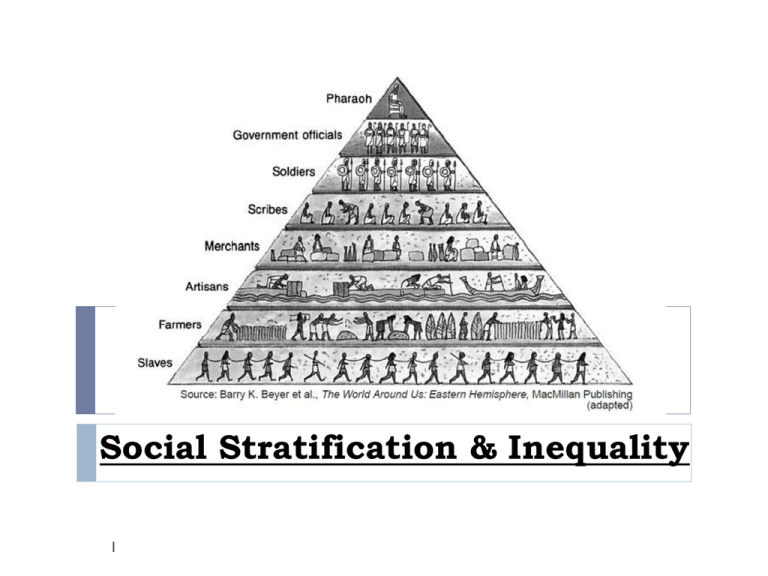
Image: studylib.net
3. The Meaning of Social Stratification
Social stratification has a profound impact on our lives. It influences our life chances, our access to opportunities, and our sense of self. It also shapes the way we interact with others and how we view the world. Individuals from different social classes often have vastly different experiences and perspectives. While the wealthy may enjoy a lifestyle of privilege and ease, those in lower classes may struggle to meet basic needs and may face social and economic barriers to achieving their aspirations. The consequences of social stratification can be vast and far-reaching, affecting everything from health outcomes to political participation.
4. Systems of Social Stratification
Social stratification exists in all societies, but the systems that create it vary widely. Some societies are highly stratified, with vast differences in wealth, power, and status, while others are more egalitarian, with a relatively narrow gap between the rich and the poor. Some common systems of social stratification include:
- Caste System: This system, prevalent in some parts of South Asia, is based on hereditary status. Individuals are born into a specific caste, and their social position is rigidly determined by their birth. There is little or no social mobility within a caste system.
- Class System: This system, prevalent in most modern societies, is based on a combination of factors, including income, wealth, occupation, and education. While there is some social mobility within a class system, it can be difficult to move between classes.
- Estate System: This system, common in feudal societies, was based on a rigid hierarchy of land ownership and social privileges. The nobility held vast landholdings and enjoyed political and legal power, while peasants were tied to the land and subject to the will of their lords.
5. The Impact of Social Stratification on Individuals and Society
Social stratification has a profound impact on individuals and societies as a whole. Some of the key impacts include:
- Limited Opportunities: Individuals from lower social classes often face limited opportunities for education, employment, and advancement. This can lead to a cycle of poverty and disadvantage, perpetuating social inequality.
- Social Mobility: The ability to move between social classes varies significantly between societies. Some societies offer greater opportunities for social mobility, while others have a rigid social structure that limits upward movement.
- Social Conflict: Inequalities in wealth, power, and status can lead to social conflict and unrest. This can manifest in various forms, including protests, strikes, and revolutions.
- Social Stability: Some argue that a certain level of social stratification is necessary for social order and stability. This view suggests that a hierarchy of power allows for the efficient allocation of resources and the maintenance of social cohesion.
Understanding the Trends and Developments in Social Stratification
Social stratification is a dynamic concept, constantly evolving in response to changes in society. Several trends and developments are shaping the landscape of social stratification in the modern world. The rise of globalization, technological advancements, and changing demographics are all having a significant impact on the way we understand and define social classes.
One noteworthy trend is the increasing wealth inequality. The gap between the rich and the poor is widening in many parts of the world, fueled by factors such as globalization, automation, and economic policies that favor the wealthy. This growing gap is raising concerns about social cohesion and the sustainability of economic systems. Another trend is the emergence of new social classes, driven by technological advancements and the rise of the digital economy. The rise of the “creative class” and the “knowledge economy” has created new opportunities for those with specialized skills and knowledge, while also highlighting the challenges faced by those who have been left behind in the digital revolution.
Expert Advice for Navigating Social Stratification
Social stratification is a complex and multifaceted issue. Individuals can play an active role in understanding and addressing its impact. Here’s some expert advice:
- Be Informed: Educate yourself about social stratification and its impact on society. Read books, articles, and watch documentaries that explore the topic. Engage in conversations with people from diverse backgrounds to gain insights into their lived experiences.
- Challenge Biases: Be mindful of your own biases and preconceived notions about social classes. Recognize that stereotypes and prejudices can perpetuate social inequality. Challenge stereotypes and work towards greater understanding and empathy.
- Support Social Justice: Advocate for policies and programs that promote social justice and equality. Support organizations working to alleviate poverty, expand educational opportunities, and address social inequalities.
By understanding the dynamics of social stratification, we can work towards creating a more just and equitable society. It’s about recognizing the challenges and opportunities that arise from the unequal distribution of resources, power, and prestige in our world. By embracing a critical perspective and working towards positive change, we can strive for a future where everyone has the chance to thrive, regardless of their social background.
Frequently Asked Questions About Social Stratification
Q: Is social stratification inevitable?
A: While some believe that social stratification is inevitable, others argue that social inequality is a product of human choices and systems. There are different perspectives on this issue, and it’s a matter of continued debate and discussion.
Q: What are the benefits of social stratification?
A: Advocates for social stratification argue that it provides incentives for individuals to work hard and achieve success, leading to greater productivity and innovation. They also suggest that a certain level of inequality may be necessary for social order and stability.
Q: What are the drawbacks of social stratification?
A: Critics of social stratification argue that it leads to inequality of opportunity, limited social mobility, and social conflict. They believe that it undermines democratic values and creates a system where resources are unfairly distributed, perpetuating poverty and disadvantage.
Q: What can I do to address social stratification?
A: You can contribute to addressing social stratification by supporting policies that promote social justice and equality, educating yourself about the issue, and challenging stereotypes and prejudices. You can also volunteer your time or donate to organisations working to alleviate poverty and provide opportunities for disadvantaged communities.
What Does Social Stratification Mean
Conclusion
Social stratification is a complex and multifaceted concept that shapes our lives and societies. Understanding the layers of social stratification and its impact can empower us to act on creating a more just and equitable society. The key lies in being informed, challenging biases, and supporting social justice initiatives.
Are you interested in learning more about social stratification and its impact on your community?



/GettyImages-173599369-58ad68f83df78c345b829dfc.jpg?w=740&resize=740,414&ssl=1)


