Imagine a young child, eager to learn and grow. Their parents, their primary agents of socialization, are their first teachers, guiding them through the world. But what happens as the child ventures beyond the home, exploring new environments and encountering diverse individuals? This is where secondary agents of socialization step in, playing a crucial role in shaping our identities, values, beliefs, and behaviors.

Image: www.vrogue.co
From the classroom to the workplace, from the playground to the political arena, secondary agents of socialization are the institutions and groups that influence us beyond our immediate families. They provide us with knowledge, skills, and perspectives, broadening our understanding of the world and contributing to our personal development. But how do these secondary agents work, and what impact do they have on our lives?
Exploring the Realm of Secondary Agents
Secondary agents of socialization are distinct from primary agents—our families—in their purpose and approach. While primary agents prioritize basic needs, emotional development, and foundational values, secondary agents focus on more specialized and contextualized learning. They teach us about specific roles, expectations, and behaviors within particular settings.
These agents can encompass a wide range of institutions and groups:
- Educational Institutions: Schools, universities, and training programs instill knowledge, skills, and social norms. They expose us to various perspectives, teach us how to think critically, and prepare us for future roles in society.
- Peers: Friends, classmates, and colleagues provide a sense of belonging, influence our interests and behaviors, and contribute to our social identity.
- Media: Television, movies, music, social media, and other forms of media shape our views, beliefs, and perceptions of the world. They introduce us to different cultures, values, and lifestyles.
- Workplace: Our jobs teach us about professional conduct, teamwork, and organizational structures. They shape our work ethic and contribute to our sense of self.
- Religious Institutions: Churches, temples, and mosques provide moral guidance, spiritual direction, and a sense of community. They influence our values, beliefs, and behaviors.
- Government and Law: Laws, regulations, and political systems establish social norms, protect individual rights, and shape our understanding of citizenship.
- Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs): Community groups, advocacy organizations, and social movements provide platforms for change, promote social justice, and influence public opinion.
The Impact of Secondary Agents on our Lives
Secondary agents of socialization play a vital role in our personal and social development. They:
- Expand our Knowledge and Skills: Educational institutions are the primary source of formal knowledge and skill development, but other agents, such as workplaces and peer groups, also contribute to our learning.
- Shape Our Values and Beliefs: Media, religious institutions, and social groups influence our perspectives on the world, influencing our values and shaping our beliefs.
- Develop Our Social Identity: Peer groups, schools, and workplaces foster a sense of belonging and shape our social identities by providing us with roles, expectations, and opportunities for interaction.
- Prepare Us for Roles in Society: Educational institutions and workplaces equip us with the knowledge, skills, and social norms necessary to navigate various social roles, such as employees, citizens, and consumers.
- Contribute to Social Change: NGOs, social movements, and political institutions work to create social change by challenging existing norms and advocating for new ideas, policies, and practices.
The Evolving Landscape of Secondary Agents
The world of secondary agents of socialization is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, social changes, and globalization. The rise of social media, for example, has created new platforms for social interaction, influencing our communication styles, perceptions of reality, and relationships with others. The increasing interconnectedness of societies through globalization has also exposed us to different cultures, values, and perspectives, expanding our understanding of the world.
The impact of these changes is complex and multifaceted. On the one hand, they offer new opportunities for learning, connection, and social change. On the other hand, they also raise concerns about misinformation, echo chambers, and the influence of algorithms on our perceptions and behaviors. Navigating this evolving landscape requires critical thinking, media literacy, and a commitment to seeking diverse perspectives.
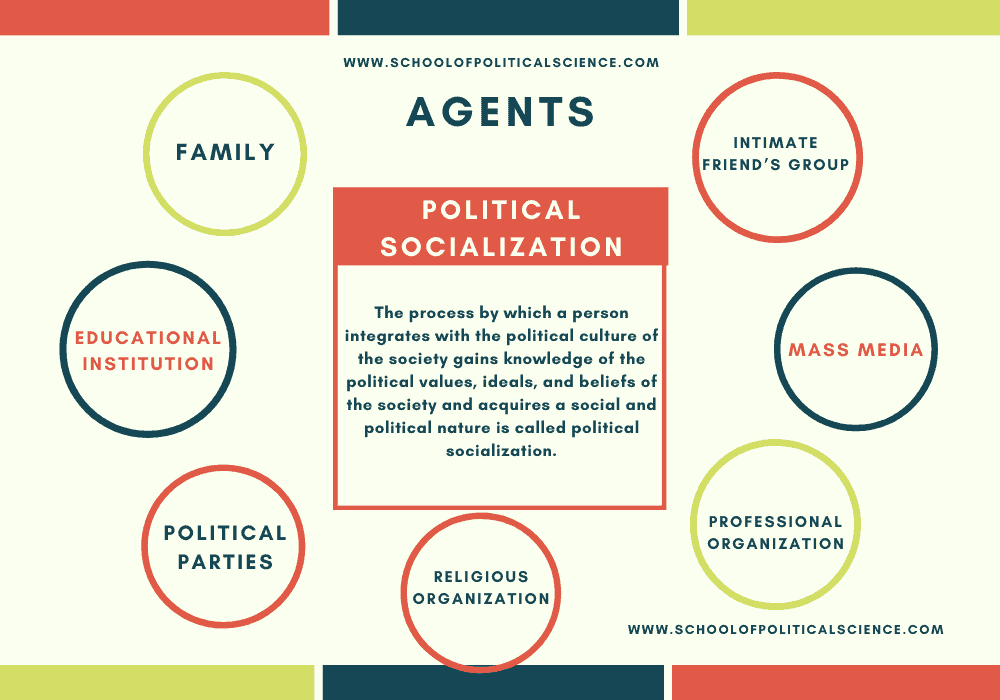
Image: schoolofpoliticalscience.com
Tips for Navigating the World of Secondary Agents
Understanding secondary agents of socialization is crucial for personal growth and societal well-being. Here are some tips for navigating this complex landscape:
- Be Aware of Your Surroundings: Pay attention to the messages you receive from various sources, considering the biases and perspectives that shape these messages.
- Develop Critical Thinking Skills: Question information, analyze arguments, and evaluate evidence before forming conclusions.
- Seek Diverse Perspectives: Engage with different ideas and opinions, both online and offline, to broaden your understanding of the world.
- Be Media Savvy: Understand how media platforms work, be aware of clickbait and propaganda, and critically evaluate the information you encounter online.
- Cultivate Strong Relationships: Build meaningful connections with individuals from diverse backgrounds, learn from their experiences, and challenge your own assumptions.
- Embrace Lifelong Learning: Continuously seek new information, knowledge, and skills to stay informed and adapt to a changing world.
These tips are essential for navigating the complex world of secondary agents of socialization. It’s a journey of ongoing learning, adaptation, and critical engagement with the information and influences that shape our lives.
FAQ
Q: How do secondary agents influence our values?
A: Secondary agents, particularly media, religious institutions, and peer groups, shape our values by presenting us with different perspectives, moral frameworks, and social norms. This exposure often leads us to adopt certain values, beliefs, and behaviors.
Q: What is the difference between primary and secondary socialization?
A: Primary socialization primarily occurs within the family, and it focuses on teaching basic social skills and values. Secondary socialization takes place in broader social settings, including schools, workplaces, and peer groups, and it emphasizes more specialized knowledge, skills, and roles within society.
Q: How can I identify the influence of secondary agents on my own life?
A: Reflect on your beliefs, values, and behaviors. Consider where you learned these things, and try to identify the agents of socialization that played a role in shaping your perspectives.
Secondary Agents Of Socialization
Conclusion
Secondary agents of socialization are essential for our personal development and integration into society. Understanding their influence is crucial for navigating our ever-changing world. By developing critical thinking skills, seeking diverse perspectives, and embracing lifelong learning, we can navigate the world of secondary agents with knowledge, awareness, and a commitment to personal growth.
Are you interested in exploring the influence of secondary agents on your life? Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below!



/GettyImages-173599369-58ad68f83df78c345b829dfc.jpg?w=740&resize=740,414&ssl=1)


