Imagine a world where your social standing is determined solely by your birthright. You’d be a prince or a pauper, a scholar or a laborer, all based on who your parents were. This was the reality for many throughout history. But as societies evolved, so too did the concept of status. Today, we often hear about “achieved status,” a term that captures the idea that we can shape our own positions in society through our efforts and accomplishments.

Image: webapi.bu.edu
This concept is fundamental to understanding how societies function and how individuals navigate their social worlds. It’s a powerful reminder that while our backgrounds play a role, our actions and choices hold significant weight in determining our place in society. In this blog post, we’ll delve deeper into the concept of achieved status in sociology, exploring its meaning, its impact, and its implications for our understanding of social mobility and individual agency.
The Essence of Achieved Status
In simplest terms, achieved status refers to a social position that is earned or acquired based on an individual’s efforts, skills, knowledge, or choices. It stands in contrast to “ascribed status,” which is a social position assigned to an individual at birth or involuntarily. Examples of ascribed status include gender, race, or family lineage. However, achieved status highlights the dynamic nature of social structures, acknowledging that individuals can change their positions within society through their actions.
Understanding this distinction is key to recognizing how societies evolve. While ascribed status emphasizes the role of tradition and inherited social hierarchy, achieved status underscores the potential for upward mobility and personal achievement. This concept has profound implications for our understanding of social mobility, social inequality, and the role of individual agency in shaping societal structures.
Examples of Achieved Status in Action
The concept of achieved status finds its expression in various aspects of our social lives. Let’s consider some prominent examples:
1. Education and Career
One of the most common ways individuals achieve higher status is through education and career progression. Obtaining a college degree, pursuing advanced degrees, or climbing the corporate ladder are all examples of achieving social recognition through hard work and dedication. Your qualifications and achievements in your chosen profession are central to your social standing.
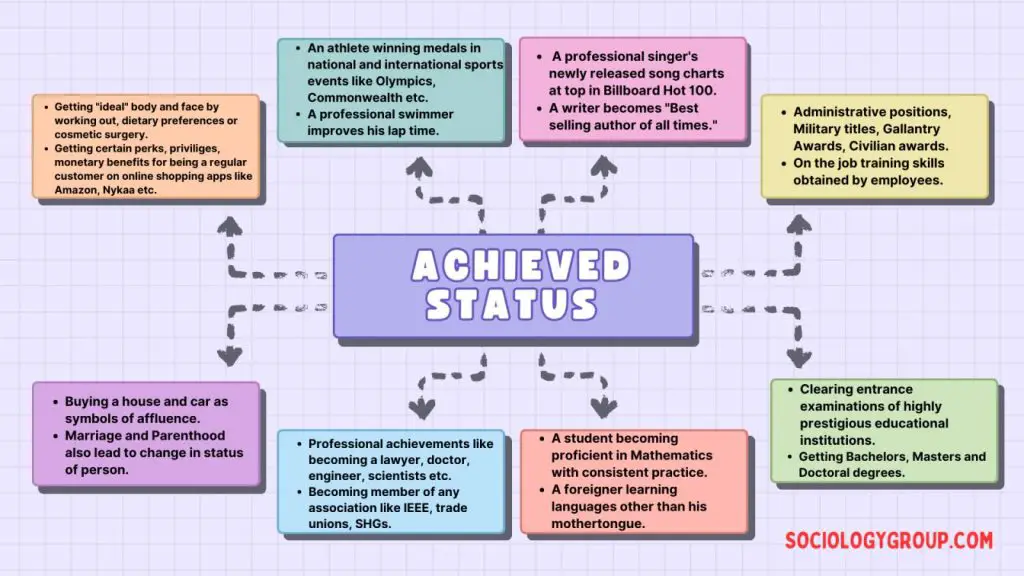
Image: www.sociologygroup.com
2. Artistic and Cultural Accomplishments
Beyond the professional realm, individuals can achieve status through their artistic and cultural contributions. For example, becoming a renowned musician, writer, painter, or actor can elevate your social standing within specific communities. Your creative prowess and talent can earn you respect, recognition, and a unique social position.
3. Social Activism and Advocacy
Social activism and advocacy often lead to the achievement of status. Individuals who dedicate themselves to causing positive social change, fighting for marginalized groups, or advocating for specific causes gain recognition and respect. Their contributions to society and their commitment to social justice can elevate their status and position them as influential figures within their communities.
The Implications of Achieved Status
The notion of achieved status holds significant implications for our understanding of social dynamics and societal structures:
1. Social Mobility and Opportunity
Achieved status highlights the possibility of social mobility, suggesting that individuals can move up or down in the social hierarchy based on their efforts. It underscores the role of individual agency in determining one’s social standing. Societies that emphasize achievement over ascription tend to have greater social mobility and provide more opportunities for upward movement.
2. Meritocratic Ideals
The concept of achieved status supports the idea of a meritocracy, where individuals are rewarded based on their abilities, talents, and hard work. It aligns with the principle that success and social standing should be earned, not inherited. However, it’s crucial to recognize that meritocratic ideals can be challenged by factors such as systemic biases and unequal access to opportunities.
3. The Role of Social Capital
While achieved status emphasizes individual effort, it’s important to acknowledge the role of social capital. This refers to the networks, relationships, and social connections that individuals leverage to achieve their goals. Access to social capital, including influential mentors, networks of contacts, and shared resources, can significantly influence one’s ability to achieve status.
Trends and Developments
The concept of achieved status is constantly evolving, influenced by contemporary societal dynamics and changes in the nature of work, technology, and global interconnectedness. Here are some key trends:
1. The Rise of the Gig Economy
The rise of the gig economy, with its emphasis on freelance work and project-based assignments, challenges traditional notions of career progression and social status. In this environment, individuals may achieve status based on their specific skills, expertise, and reputation within their network. However, it also raises concerns about job security, income stability, and the challenges of establishing a secure social position.
2. The Power of Social Media
Social media platforms have transformed the ways individuals achieve status and recognition. Online influencers, bloggers, and content creators can garner considerable influence, build significant followings, and earn a living through their online presence. The ability to build a personal brand and cultivate an online community can contribute to the achievement of status in the digital age.
3. The Importance of Education
Despite the changing landscape of work, education remains a key factor in achieving status. As technology continues to advance and the demand for skilled workers grows, higher education and specialized skills are increasingly crucial for career advancement and social mobility. However, access to quality education remains unequal, reinforcing existing social inequalities and posing challenges for achieving status for individuals from marginalized backgrounds.
Expert Advice for Achieving Status
Drawing on the insights discussed above, here are some practical tips for individuals seeking to achieve status in their social spheres:
1. Invest in Your Skills and Education
Continuously invest in your skills and education to stay competitive in the job market. Pursue professional development opportunities, acquire new skills, and seek out mentorship from experienced professionals. A robust skillset and knowledge base will enhance your career prospects and contribute to your social standing.
2. Build and Leverage Your Networks
Cultivate strong relationships with individuals who share your interests, values, and professional goals. Attend industry events, connect with colleagues online, and engage with mentors and professionals in your field. Networking can open doors to new opportunities and provide valuable support in your pursuit of achieving status.
3. Embrace Social Media Strategically
Use social media strategically to build your personal brand, share your expertise, and connect with others in your field. Create content that showcases your skills, knowledge, and accomplishments. Build a strong online presence and engage with your audience to enhance your visibility and social influence.
4. Be Passionate and Committed
Passion and commitment are essential for achieving status. Find a career or a cause that genuinely excites you and dedicate yourself to making a meaningful contribution. Your enthusiasm and dedication will inspire others and earn you respect and recognition.
5. Never Stop Learning and Growing
The world is constantly changing, and the pursuit of achieving status is a lifelong endeavor. Stay curious, seek out new knowledge, and adapt to the changing landscape of the workplace and society as a whole. Continuous learning and personal growth are key to maintaining relevance and achieving long-term success.
FAQs on Achieved Status
Q: Is achieved status the only way to gain social standing?
A: While achieved status is significant, it’s not the sole determinant of social standing. Social factors like family background, wealth, and social connections can influence one’s position, even if they weren’t earned through individual effort.
Q: Can someone lose achieved status?
A: Absolutely. Achieved status isn’t a permanent fixture. If an individual loses their expertise, fails to keep up with the changing demands of their field, or engages in unethical behavior, they can lose the respect and recognition they previously earned.
Q: How does achieved status impact social mobility?
A: Achieved status acts as a key driver of social mobility. It provides avenues for upward movement through education, hard work, and personal achievement. However, it’s crucial to recognize that systemic inequalities and structural barriers can limit social mobility for some individuals.
Achieved Status Sociology
Conclusion
Understanding achieved status is crucial for grasping the complexities of social dynamics. It reminds us that while our backgrounds shape us, our efforts play a vital role in determining our place in society. By investing in our skills, building our networks, and embracing a growth mindset, we can actively shape our own destinies. Are you interested in exploring more about how achieved status shapes our lives and how we can use this concept to navigate the complex social world we live in? Let me know in the comments below!



/GettyImages-173599369-58ad68f83df78c345b829dfc.jpg?w=740&resize=740,414&ssl=1)


