Imagine a world without bridges, skyscrapers, or even automobiles. It’s a world where complex structures cannot be assembled, and everyday objects become impossible to create. This is the world we would live in without welding and joining, the invisible forces that bind materials together, shaping the very fabric of our modern civilization.
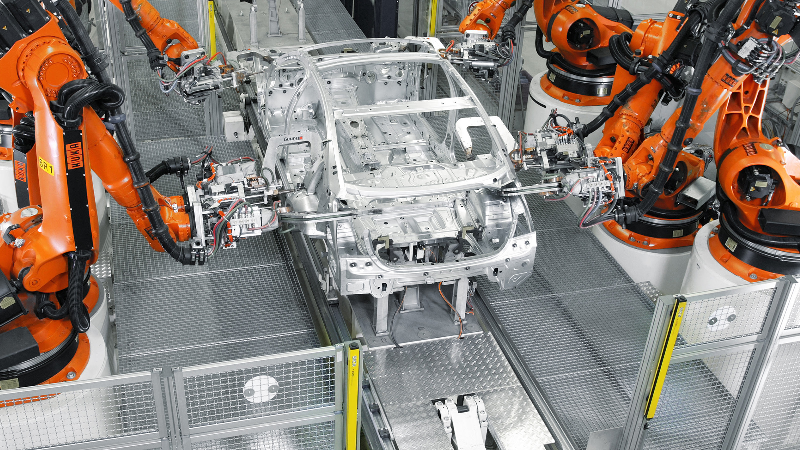
Image: www.lightmetalage.com
Welding and joining are far more than just a way to connect pieces of metal. These processes delve into the complex science of metallurgy and materials, harnessing the power of heat, pressure, and chemical reactions to create bonds that are as strong as the materials themselves. This article will delve into the captivating world of welding and joining, uncovering the scientific principles that underpin this crucial technology and exploring its revolutionary impact on our world.
A History of Fusion: From Ancient Times to Modern Marvels
The history of welding is as old as human civilization itself. Early blacksmiths used primitive methods like forge welding, hammering heated pieces of metal together to create a bond. As societies progressed, so did the need for more sophisticated joining techniques. Over centuries, advancements in materials science and technology led to the development of numerous welding processes, each tailored to specific applications and materials.
Unveiling the Secrets: The Science of Welding and Joining
At its core, welding revolves around manipulating the structure of materials at the atomic level. The process involves melting and fusing two or more pieces of material, creating a bond that is as strong, if not stronger, than the original material itself. This seemingly simple process hinges on complex scientific principles:
- Metallurgy: The science of metals forms the foundation of welding. Understanding the properties of different metals, their melting points, and their behavior under heat is paramount to achieving successful welds.
- Thermal Dynamics: Heat is the driving force behind most welding processes. The application of heat, whether through an open flame or an electric arc, alters the molecular arrangement of the material, allowing the atoms to intermix and form a bond.
- Physical Chemistry: Chemical reactions involved in welding processes play a significant role in the final bond strength. The presence of gases, fluxes, and other chemicals can influence the way metals interact, affecting the quality of the weld.
A Symphony of Methods: Exploring the Diverse World of Welding
The versatility of welding lies in its myriad processes, each designed for specific applications and materials. From the familiar arc welding used in construction to the high-precision laser welding employed in the aerospace industry, every method utilizes unique techniques and scientific principles:
- Arc Welding: This widely used method generates an electric arc between an electrode and the workpiece to melt the metal.
- Gas Welding: This traditional process employs a flame generated by burning a mixture of oxygen and fuel gases to melt the materials.
- Resistance Welding: Utilizing a high current flow through the workpiece, this method creates heat and pressure to fuse the materials.
- Laser Welding: Employing a focused laser beam, this process offers extreme precision and minimal heat distortion, making it ideal for intricate applications.
- Friction Welding: This unique method uses friction generated by rotating one workpiece against another to melt and fuse the materials.

Image: www.youtube.com
Beyond the Weld: The Role of Joining Technologies
While welding is the most recognized joining technique, other methods play critical roles in various applications, each harnessing unique scientific principles:
- Soldering: This process uses a low-melting-point alloy to join two or more surfaces, often used in electrical and electronic applications.
- Brazing: A similar process to soldering, but using a higher melting point alloy, suitable for joining stronger materials.
- Adhesive Bonding: Utilizing specialized adhesives, this method offers high bond strength and flexibility, particularly useful for lightweight materials.
- Mechanical Joining: This involves mechanical fasteners like screws, rivets, and bolts to create a secure connection.
Bridging the Gap: The Impact of Welding and Joining on Our World
The impact of welding and joining technologies extends far beyond the construction industry. These processes are the lifeblood of modern manufacturing, contributing to the creation of everything from cars and airplanes to medical devices and smartphones:
- Transportation: Welding and joining are essential in the automotive and aerospace industries, ensuring the structural integrity of vehicles and aircraft.
- Construction: Building bridges, skyscrapers, and infrastructure rely heavily on welding techniques to create robust and durable structures.
- Manufacturing: From power plants to factories, welding and joining are crucial for assembling machinery, equipment, and industrial tools.
- Electronics and Technology: The production of electronics, including computers, smartphones, and medical devices, relies on welding and joining technologies for internal circuits and components.
Looking Ahead: Trends and Innovations in Welding and Joining
The world of welding and joining is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in materials science, automation, and digital technologies. These trends are pushing the boundaries of what’s achievable with welding and joining:
- Robotics and Automation: Robots are increasingly used in welding applications, improving efficiency, precision, and safety.
- Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): This revolutionary technology is transforming welding and joining. 3D printing allows for the creation of complex structures with intricate designs and custom geometries.
- Advanced Materials: The development of new materials, such as composites and high-strength alloys, requires new welding and joining techniques to achieve optimal performance.
- Smart Welding: Incorporating sensors, data analytics, and artificial intelligence into welding processes enables real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and improved quality control.
The Art of the Weld: Expert Insights and Actionable Tips
Mastering the art of welding requires both theoretical knowledge and practical experience. Here are insights from experienced welders to enhance your skills:
- Understanding Materials: Understanding the unique properties of different metals is essential for choosing the right welding process and parameters.
- Proper Technique: A firm grasp of welding techniques, including arc length, travel speed, and electrode angle, is fundamental for achieving consistent and quality welds.
- Safety First: Safety precautions must always be prioritized. Wearing personal protective equipment like gloves, masks, and protective clothing is essential.
- Continuous Learning: The world of welding is constantly evolving. Embrace continuous learning through books, online resources, and workshops to stay ahead of the curve.
Science And Technology Of Welding And Joining
A World Without Limits: Embracing the Future of Welding and Joining
Welding and joining are not merely technical processes; they are the cornerstones of innovation and progress, enabling us to build a better future. As technology continues to advance, welding and joining will continue to play a vital role in shaping our world. The next time you encounter a bridge, a car, or even a simple piece of jewelry, take a moment to appreciate the unseen forces at work, the science and technology that bind materials together and drive our world forward.



/GettyImages-173599369-58ad68f83df78c345b829dfc.jpg?w=740&resize=740,414&ssl=1)


