Imagine a world without smartphones, self-driving cars, or the internet. It’s hard to fathom, isn’t it? These groundbreaking technologies, and countless others, are a testament to the ingenuity and innovation within the realms of electrical engineering and computer science. But behind the sleek designs and sophisticated algorithms lies a complex legal framework: patent prosecution. This article delves into the intricate world of protecting intellectual property in these rapidly evolving fields, exploring the challenges, strategies, and triumphs of securing patents for electrical engineering and computer science innovations.
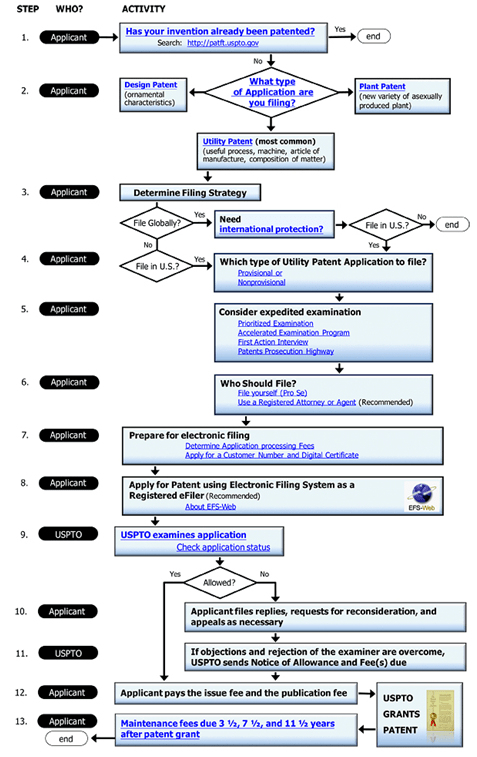
Image: www.maxval.com
Patent prosecution, the process of obtaining a patent, is crucial for inventors and organizations in electrical engineering and computer science. A patent grants the inventor exclusive rights to their invention for a specific period, allowing them to control its use, manufacture, and sale. This protection enables investment, commercialization, and competitive advantage in a landscape where technology is constantly evolving.
The Journey of a Patent: From Idea to Grant
1. Invention Disclosure and Patentability Assessment
The journey begins with a detailed invention disclosure, a clear and concise documentation of the invention’s features, functionality, and potential applications. This disclosure is then subjected to a rigorous patentability assessment. Patent attorneys and agents with expertise in electrical engineering and computer science analyze the invention against existing prior art, evaluating its novelty, inventiveness, and utility.
2. Drafting the Patent Application
Once patentability is confirmed, the patent application takes shape. This crucial document, drafted by skilled patent professionals, outlines the invention in meticulous detail, employing technical language and specific claim language to define the invention’s scope and boundaries. The application includes a detailed description of the invention, its function, and how it differs from existing technologies. It also contains claims, which represent the legal boundaries of the invention’s protection.

Image: sagaciousresearch.com
3. Filing the Patent Application
The patent application, complete with drawings, specifications, and claims, is filed with the relevant patent office. In the United States, this is the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO). The filing date marks the official start of the patent prosecution process.
4. Examination and Response to Office Actions
The patent application undergoes a thorough examination by patent examiners at the USPTO. Examiners meticulously analyze the application, comparing it against existing prior art, to determine whether the invention meets the criteria for patentability. This process typically involves several rounds of communication between the applicant and the examiner. The applicant must address any concerns raised by the examiner through formal responses, amending the application or arguing the patentability of their invention. This phase requires a deep understanding of patent law, technical knowledge, and strong communication skills.
Challenges and Considerations
The landscape of patent prosecution in electrical engineering and computer science is constantly evolving. The rapid pace of innovation and the increasing complexity of technologies present unique challenges:
- Rapid Obsolescence: In a field where advancements occur at lightning speed, patents often face the challenge of becoming obsolete before their full potential can be realized. This requires strategic planning and continuous monitoring of the technological landscape to ensure the patent remains relevant.
- Prior Art Search and Analysis: Identifying and analyzing relevant prior art is crucial to demonstrate the invention’s novelty and non-obviousness. With an abundance of scientific publications, patents, and other sources of technological information, this task can be daunting and requires specialized expertise.
- Claim Drafting: Claim language is the backbone of a patent, defining the legal scope of protection. Accurately drafting claims that capture the invention’s essence while being broad enough to encompass future variations is a delicate art.
- Interference Proceedings: When multiple inventors claim rights to similar inventions, interference proceedings may occur. These complex legal battles require extensive preparation, strategy, and evidence to prove priority and establish rightful ownership.
The Importance of Collaboration
Navigating the complex legal landscape of patent prosecution requires a collaborative approach. Inventors, researchers, and legal professionals must work together to achieve successful patent protection. Patent attorneys and agents play a crucial role in guiding the process, leveraging their expertise in patent law, strategic thinking, and technical understanding to secure strong patent rights. Their involvement is essential for:
- Strategic Patent Planning: Patent attorneys can help develop a comprehensive patent strategy tailored to the specific needs and goals of the inventor or organization. This includes identifying potential patent applications, prioritizing inventions, and determining the optimal filing strategy.
- Technical Expertise: Patent attorneys with expertise in electrical engineering and computer science can effectively translate technical complexities into legally sound language, ensuring accurate and comprehensive patent applications.
- Negotiation and Advocacy: Patent attorneys act as skilled negotiators and advocates during the prosecution process, strategically communicating with the patent office and diligently responding to office actions. Their expertise in patent law and negotiation skills help secure the strongest possible patent protection.
Trends and Developments
The field of electrical engineering and computer science patent prosecution is constantly evolving, fueled by rapid technological advancements and changing legal landscapes. Some notable trends include:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning are revolutionizing the way patent prosecution is conducted. These technologies are being used for tasks such as prior art search, claim analysis, and patent portfolio management. AI-powered tools are helping legal professionals streamline processes, identify potential risks, and improve efficiency.
- Software Patents: Software inventions are increasingly becoming the subject of patent protection. The USPTO has developed specific guidelines for evaluating software patents, focusing on the inventive concept and its practical application rather than simply on the code itself.
- Global Patent Protection: With technology transcending national borders, inventors are seeking patent protection in multiple countries. Navigating different patent laws and procedures requires global expertise and international collaboration.
Electrical Engineering And Computer Science Patent Prosecution
Conclusion
Securing patent protection for innovations in electrical engineering and computer science is essential for driving progress, attracting investment, and establishing a competitive edge. While the journey of patent prosecution can be complex and challenging, it is a rewarding endeavor that empowers inventors and organizations to control their intellectual property and shape the future of technology. By understanding the process, collaborating with skilled patent professionals, and staying informed about evolving trends, inventors can successfully navigate the patent landscape and protect their valuable inventions.



/GettyImages-173599369-58ad68f83df78c345b829dfc.jpg?w=740&resize=740,414&ssl=1)


