Are you the type to spend an afternoon leisurely perusing a menu, savoring the aromas of freshly prepared dishes, and engaging in lively conversation over a meticulously crafted meal? Or do you prioritize speed and affordability, opting for a quick bite that fits your busy schedule and budget? The simple act of eating can spark a debate between two distinct culinary landscapes: the world of restaurants and the realm of fast food.

Image: www.alharirigroup.com.tr
While both provide nourishment, their approach to food, service, and the overall dining experience diverge significantly. Understanding these differences can empower you to make informed choices that align with your personal preferences and needs. This article delves into the fascinating world of restaurants versus fast food, exploring their history, characteristics, and the factors that shape your dining decisions.
The Evolution of Culinary Choices
The Rise of Fast Food: A Shift in Culture
The concept of fast food traces its roots back to the 19th century, with the advent of lunch counters and “quick lunch” establishments catering to urban populations. However, the birth of the modern fast-food industry is often attributed to the 1940s and the emergence of drive-in restaurants, fueled by the rise of automobile culture. The iconic McDonald’s, founded in 1940, pioneered the concept of standardized menus, efficient production lines, and a focus on speed and affordability. Fast food’s appeal to the post-World War II generation, seeking convenience and efficiency, propelled its growth throughout the 20th century.
The Evolution of the Restaurant Scene: A Celebration of Cuisine
Parallel to the rise of fast food, restaurants evolved from casual eateries to sophisticated dining establishments. The post-war period saw the emergence of fine dining restaurants, characterized by their emphasis on gourmet cuisine, elegant settings, and impeccable service. As culinary trends shifted, restaurants became places to experiment with new flavors, explore global cuisines, and share memorable experiences with friends and family. The restaurant industry embraced innovation, diversifying its offerings to cater to a wide range of palates and budgets, from casual cafes to Michelin-starred temples of gastronomy.
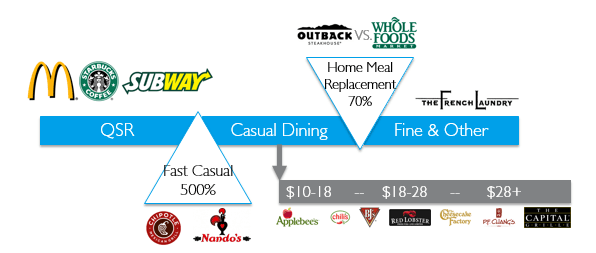
Image: aaronallen.com
Defining the Differences: A Culinary Comparison
Fast Food: Speed and Affordability
Fast food is defined by its emphasis on speed and affordability. It serves up simple, often standardized dishes, optimized for quick preparation and assembly. The focus is on efficient service, prioritizing the delivery of food as quickly as possible, often within minutes. Fast food establishments typically use assembly line production methods, employing pre-cooked ingredients, standardized portion sizes, and limited customization options. The emphasis on affordability makes it a popular choice for budget-conscious diners, students, and busy professionals.
Restaurants: Culinary Exploration and Experience
Restaurants, on the other hand, prioritize a more immersive dining experience. They offer a wider range of cuisine, with menus often featuring seasonal ingredients, unique flavor combinations, and creative plating. Restaurants also invest in creating a specific atmosphere, ranging from cozy cafes to grand dining halls, each with their own ambiance and design. The service is more personalized and attentive, with trained staff providing recommendations, taking orders, and attending to the needs of their guests throughout the meal. Restaurants often prioritize quality over speed, allowing for longer preparation times and a focus on culinary craftsmanship.
The Pros and Cons: A Balanced Perspective
Fast Food: The Advantages of Efficiency
Fast food offers several advantages:
- Speed and convenience: Fast food provides a quick and easy meal option, ideal for those with limited time.
- Affordability: Fast food is generally more budget-friendly compared to restaurants, making it an accessible choice for various income levels.
- Wide availability: Fast food chains are widespread, ensuring readily available meals throughout the day and night.
- Consistency: Standardized recipes and preparation methods ensure consistent quality and flavor, regardless of the location.
Fast Food: The Drawbacks of Convenience
However, fast food also comes with its share of drawbacks:
- Nutritional concerns: Fast food often features high amounts of fat, sodium, sugar, and processed ingredients, potentially leading to health problems with regular consumption.
- Limited customization: Fast food menus often offer limited customization options, restricting dietary choices and preferences.
- Environmental impact: Fast food packaging and disposable serving materials contribute to environmental pollution.
- Lack of personal interaction: The focus on speed often leads to a more impersonal dining experience, with limited interactions between staff and customers.
Restaurants: The Rewards of Culinary Exploration
Restaurants offer a variety of benefits:
- High-quality ingredients: Restaurants often source fresh, seasonal ingredients and prioritize quality over quantity.
- Creative and diverse cuisine: Restaurants cater to a wide range of culinary preferences, offering everything from classic comfort food to innovative fusion dishes.
- Personalized service and ambiance: Restaurants create a more intimate and welcoming dining experience, with attentive staff and a curated atmosphere.
- Opportunities for social interaction: Restaurants provide a social setting for gathering with friends, family, or colleagues, fostering meaningful connections.
Restaurants: The Challenges of Quality and Price
Restaurants also face challenges:
- Higher prices: Restaurant meals are typically more expensive than fast food due to the use of higher quality ingredients, longer preparation times, and more personalized service.
- Variability in quality: While restaurants aim for consistency, the quality of dishes can vary depending on the chef, ingredients, and execution.
- Limited accessibility: Restaurants may not be accessible to everyone due to higher pricing and limited locations.
- Long waiting times: Restaurant meals often require longer preparation and service times, especially during peak hours.
The Future of Food: Trends and Innovations
The culinary landscape is constantly evolving, with both fast food and restaurants adapting to changing consumer demands and technological advancements. The lines between these two categories are blurring, with fast-casual restaurants emerging, offering a blend of affordability and quality. Fast food establishments are also implementing technological innovations, like mobile ordering and delivery services, to enhance convenience and cater to the tech-savvy generation.
Restaurants are embracing new culinary techniques, emphasizing local, sustainable ingredients, and offering personalized dining experiences. The rise of veganism and gluten-free diets has also driven innovation, prompting restaurants to adapt their menus to accommodate dietary restrictions and preferences. With advancements in food technology, we may see even more transformative changes in the years to come, including personalized nutrition plans, 3D-printed food, and innovative delivery systems.
Restaurant Vs Fast Food
Conclusion: Making an Informed Culinary Choice
The choice between restaurant and fast food ultimately boils down to your personal priorities and preferences. Whether you prioritize speed and affordability, or seek a culinary adventure with a personalized dining experience, both options offer unique benefits and drawbacks. The key is to make informed decisions, considering factors like budget, time constraints, dietary needs, and personal preferences. By understanding the nuances of each option, you can make the most of your culinary choices and savor the pleasures of dining, whether it’s a quick bite on the go or a leisurely meal in a welcoming atmosphere.



/GettyImages-173599369-58ad68f83df78c345b829dfc.jpg?w=740&resize=740,414&ssl=1)


