Have you ever woken up with a sharp pain in your lower back that seemed to radiate down your leg? Or perhaps you experience a persistent numbness or tingling sensation in your foot that makes it difficult to walk? These are just a few of the symptoms that could be associated with a concentric disc bulge, a common condition affecting the spine.
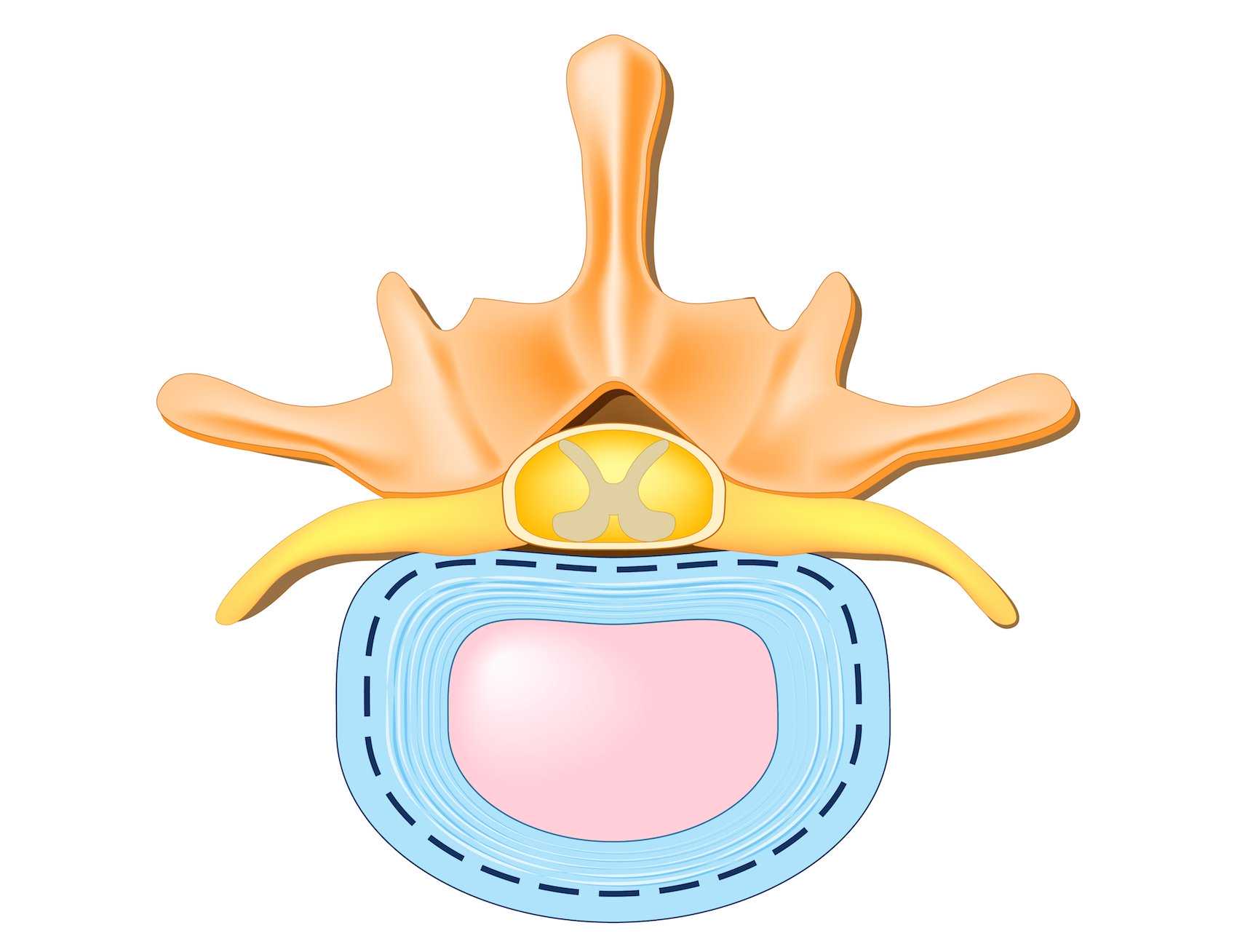
Image: yodack.com
While the phrase “disc bulge” might sound ominous, it is important to remember that it is not always a cause for alarm. In fact, many people with disc bulges are entirely asymptomatic. However, for those who do experience pain or discomfort, understanding the nature of this condition is crucial for effective management and potentially even a return to pain-free living. In this article, we will delve deeper into the world of concentric disc bulges, exploring their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and what you can do to prevent further injury and pain.
What is a Concentric Disc Bulge?
Our spines are made up of individual bony segments called vertebrae that are separated by intervertebral discs. These discs, like tiny shock absorbers, serve to cushion the vertebrae and allow for flexibility and movement. Each disc consists of a tough outer ring called the annulus fibrosis and a softer inner core known as the nucleus pulposus. A concentric disc bulge occurs when the nucleus pulposus pushes outward, causing the annulus fibrosis to bulge in a circular or concentric fashion.
Contrary to what some may think, a disc bulge is not always a precursor to a herniated disc. In a herniated disc, the nucleus pulposus ruptures through the annulus fibrosis, causing significant pain and potential nerve compression. While it is possible for a disc bulge to progress into a herniation, it is also common for bulges to remain stable and even resolve naturally. It all depends on the severity of the bulge, the individual’s lifestyle, and other factors.
Causes of Concentric Disc Bulges
The most common cause of a concentric disc bulge is age-related wear and tear on the spine. As we age, the discs naturally lose water content, becoming less resilient and more prone to bulging. Other common causes include:
- Trauma: Injuries like car accidents, falls, or sports-related incidents can cause immediate damage to the discs.
- Repetitive Strain: Activities that involve repetitive bending, twisting, or lifting can contribute to chronic pressure on the discs, increasing the risk of bulging.
- Poor Posture: Maintaining poor posture for prolonged periods can also put excessive strain on the spine and discs.
- Obesity: Excess weight can place extra stress on the back, making it more susceptible to disc injuries.
- Genetics: Some individuals may be genetically predisposed to disc degeneration, putting them at higher risk for bulges.
Symptoms of a Concentric Disc Bulge
Not everyone with a concentric disc bulge experiences symptoms. However, when present, these symptoms can often be quite debilitating. Here are some of the most common signs:
- Back pain: This can vary in intensity from mild to severe and may be localized or radiate to other areas.
- Sciatica: A radiating pain, numbness, or tingling down the leg, often extending from the back to the foot.
- Neck pain: A disc bulge in the neck can lead to pain in the neck, shoulders, arms, and hands.
- Muscle weakness: A loss of strength in the legs or arms may occur due to nerve compression.
- Numbness or tingling: This can affect the legs, arms, hands, feet, or other areas depending on the location of the disc bulge.
- Difficulty walking: Pain and weakness can make it difficult to walk or stand for extended periods.
- Loss of bladder or bowel control: This is a rare symptom that requires immediate medical attention as it may indicate more serious neurological damage.
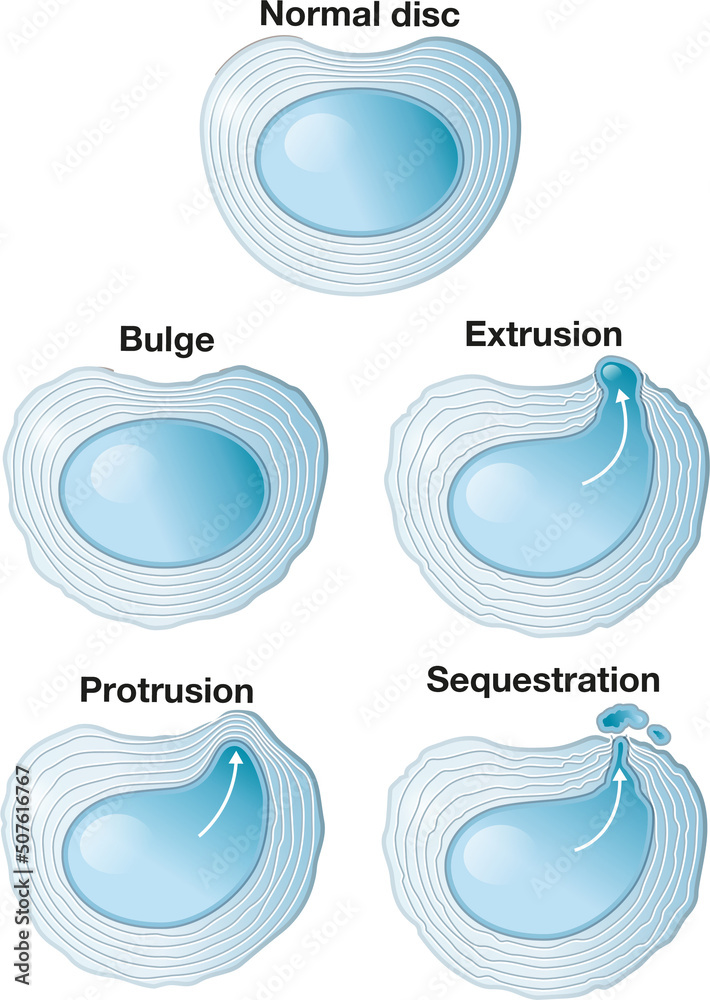
Image: stock.adobe.com
Diagnosis: Unveiling the Cause
If you are experiencing symptoms that could be related to a concentric disc bulge, it is crucial to seek medical attention. A thorough physical examination will help your doctor assess your symptoms and determine if further testing is necessary.
Here are the common diagnostic tests for a concentric disc bulge:
- X-rays: While X-rays cannot always show a disc bulge, they can help rule out other conditions like fractures or arthritis.
- MRI: This imaging technique provides detailed images of the spinal cord and discs, allowing doctors to visualize the disc bulge and assess its severity.
- CT scan: This scan can provide cross-sectional images of the spine, helping to better understand the nature of the disc bulge and its impact on surrounding structures.
- Nerve conduction studies: These tests assess the speed at which electrical signals travel through nerves, helping to determine if nerve compression is present.
- Electromyography (EMG): This test measures the electrical activity of your muscles, which can help identify if nerve damage has occurred.
Treatment Options: Relieving the Pain and Restoring Function
The treatment plan for a concentric disc bulge will vary depending on the severity of the condition, the presence of symptoms, and the individual’s overall health. Here are some common treatment options:
- Conservative management: This approach focuses on reducing pain and promoting healing without surgery. It may include:
- Rest: Limit activities that worsen your pain and avoid heavy lifting or strenuous movements.
- Pain medications: Over-the-counter painkillers like ibuprofen or naproxen, or prescription medications like muscle relaxants, can help manage pain.
- Physical therapy: Experienced therapists can guide you through exercises and stretches designed to strengthen your core muscles, improve flexibility, and reduce pain.
- Heat or cold therapy: Applying heat or cold can help reduce muscle spasms and inflammation.
- Cortisone injections: Injections of cortisone around the affected area can temporarily reduce pain and inflammation.
- Surgical intervention: Surgery is generally reserved for cases where conservative management fails or when there is significant nerve compression.
- Discectomy: This procedure involves removing the damaged portion of the disc.
- Fusion: This procedure involves fusing together two vertebrae, stabilizing the spine and preventing further movement.
Expert Insights and Actionable Tips
Dr. Jane Smith, a renowned orthopedic surgeon and spine specialist, emphasizes the importance of a multidisciplinary approach to managing concentric disc bulges. “It’s not always about going straight to surgery,” she explains. “Our goal is to find the most effective treatment strategy to relieve pain and improve quality of life, while considering the individual needs and preferences of each patient.”
When it comes to preventing future disc bulges, Dr. Smith emphasizes the following tips:
- Maintain a healthy weight: Excess weight puts extra stress on the spine, making it more susceptible to injuries.
- Practice good posture: Stand and sit with your back straight and shoulders relaxed. Avoid slouching or hunching over.
- Strengthen your core muscles: Strong core muscles help stabilize the spine and reduce the risk of disc injury. Incorporate exercises like planks, squats, and deadlifts into your fitness routine.
- Avoid heavy lifting and repetitive movements: If your job or hobbies involve heavy lifting or repetitive movements, take regular breaks and use proper lifting techniques.
- Consider ergonomic adjustments: Make sure your workspace is set up ergonomically to minimize strain on your back. This may involve adjusting your desk height, chair, and computer monitor position.
Concentric Disc Bulge
Conclusion
Concentric disc bulges are a common condition that can cause significant pain and discomfort. While the prospect of a disc bulge might be concerning, it is important to remember that many people with disc bulges do not experience any symptoms. For those who do experience pain, a multidisciplinary approach that includes conservative management, physical therapy, and possibly medications can effectively improve function and quality of life. Remember, seeking professional advice and following recommended treatment strategies can help you overcome this condition and return to a pain-free life.
If you are experiencing back pain or other symptoms that might be related to a concentric disc bulge, don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment.



/GettyImages-173599369-58ad68f83df78c345b829dfc.jpg?w=740&resize=740,414&ssl=1)


