Imagine waking up one morning with a sharp, shooting pain down your leg. You’re barely able to stand, and even the slightest movement seems to amplify the agony. This is the kind of excruciating experience that many people living with a posterior disc bulge face. A posterior disc bulge is a common cause of lower back pain and sciatica, and understanding its nuances can be the first step towards alleviating this debilitating condition.
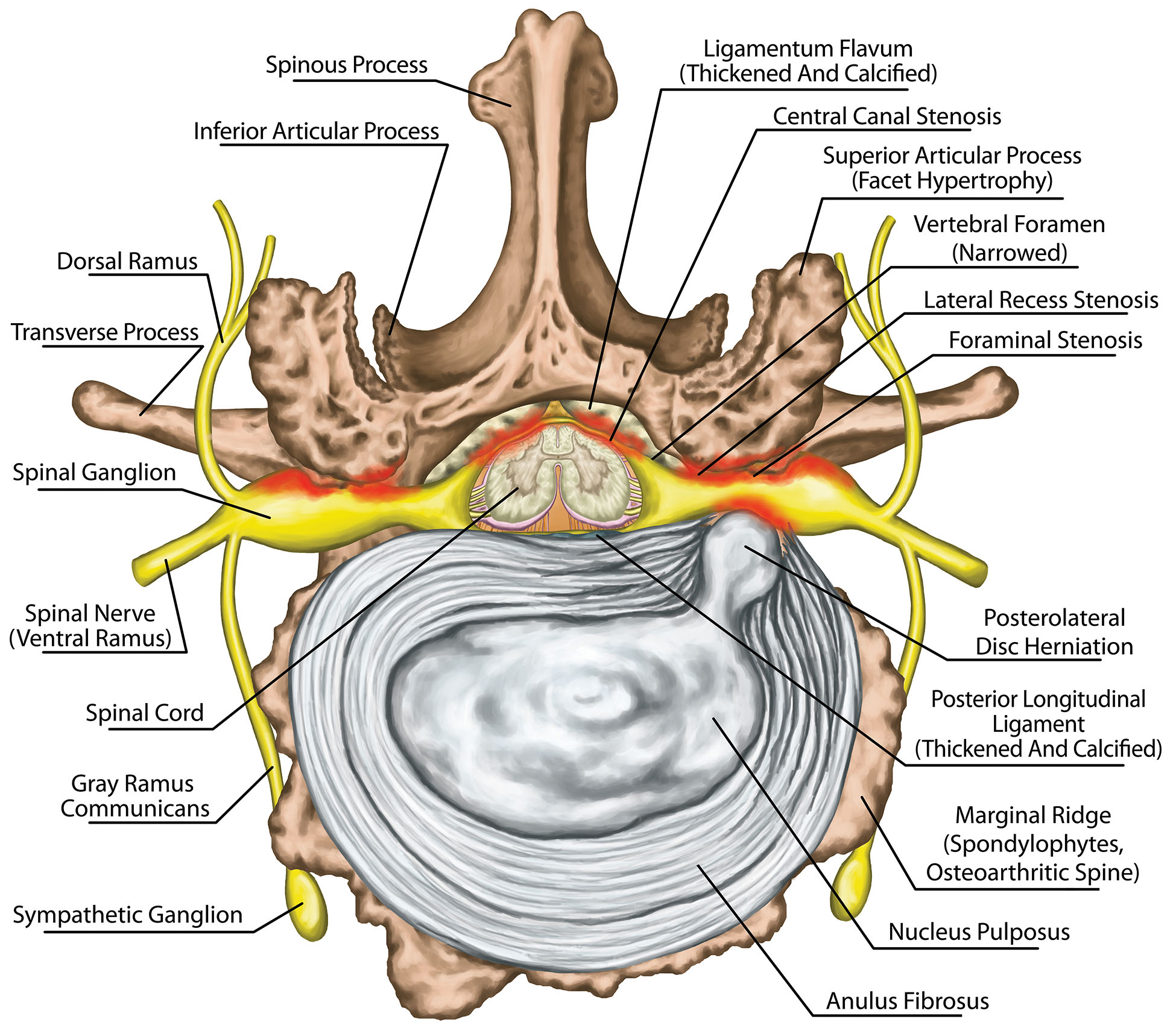
Image: ainsworthinstitute.com
This article delves into the world of posterior disc bulges, providing an in-depth exploration of their causes, symptoms, and treatment options. We’ll discuss the anatomy of the spine, the mechanics of a disc bulge, and how it impacts your daily life. We’ll also explore different treatment approaches, both conservative and surgical, offering insights into how to manage and potentially resolve this condition. By the end of this article, you’ll have a clear understanding of posterior disc bulges and be empowered with the knowledge to take proactive steps for your health.
Understanding Posterior Disc Bulges: A Deep Dive into the Anatomy and Mechanics
To comprehend posterior disc bulges, we need to first understand the anatomy of the spine. The spine, our body’s central support structure, consists of 33 individual bones called vertebrae, stacked upon one another. Between each vertebra, there are cushions called intervertebral discs, which act as shock absorbers and allow for flexibility and movement. These discs are composed of two parts: the outer ring, known as the annulus fibrosus, and the inner core, called the nucleus pulposus.
The nucleus pulposus, a jelly-like substance, provides the disc’s elasticity and cushioning. The annulus fibrosus, a tough fibrous ring, encases the nucleus and helps maintain its shape. In a healthy spine, these discs function seamlessly, allowing us to bend, twist, and lift without experiencing pain.
However, over time, these discs can wear down, leading to a variety of issues, including a posterior disc bulge. A posterior disc bulge occurs when the nucleus pulposus pushes outward through a weakened annulus fibrosus, pressing against the spinal cord or nerves that exit the spinal canal. This pressure often leads to pain, numbness, and weakness in the affected area. It’s important to understand that not all disc bulges cause symptoms. Some people may have small disc bulges that never cause any pain or discomfort.
Causes of Posterior Disc Bulge: Understanding the Triggers
A posterior disc bulge is often caused by a combination of factors. These can range from age-related wear and tear to specific activities and even genetic predispositions. Here are some of the most common contributing factors:
- Age: As we age, the water content of our intervertebral discs decreases, making them less resilient and more susceptible to bulging or herniation.
- Trauma: A sudden injury, such as a fall or car accident, can strain the discs and lead to a bulge.
- Repetitive stress: Activities that involve repeated bending, twisting, or lifting can put stress on the spine and contribute to disc degeneration. This is particularly common in occupations that involve manual labor.
- Poor posture: Maintaining poor posture over time can put excessive strain on the spine, leading to disc bulges.
- Obesity: Excess weight can put additional stress on the spine, accelerating disc wear and tear.
- Genetic predisposition: Some individuals have a genetic predisposition to weak intervertebral discs, making them more likely to develop disc bulges.
Symptoms of Posterior Disc Bulge: Recognizing the Warning Signs
The symptoms of a posterior disc bulge can range from mild to severe, depending on the severity of the bulge and the location within the spine. Here are some common symptoms:
- Lower back pain: This is often the first symptom of a posterior disc bulge, and it can vary in intensity from a dull ache to a sharp, shooting pain.
- Sciatica: A posterior disc bulge in the lower spine can compress the sciatic nerve, leading to radiating pain down the leg, often into the foot.
- Numbness or tingling: A bulging disc can also cause numbness or tingling in the legs, feet, or even the buttocks.
- Weakness: A posterior disc bulge can weaken the leg muscles, making it difficult to walk or stand for prolonged periods.
- Difficulty with bowel or bladder control: In severe cases, a posterior disc bulge can compress the nerves that control bowel and bladder function, leading to problems with control.
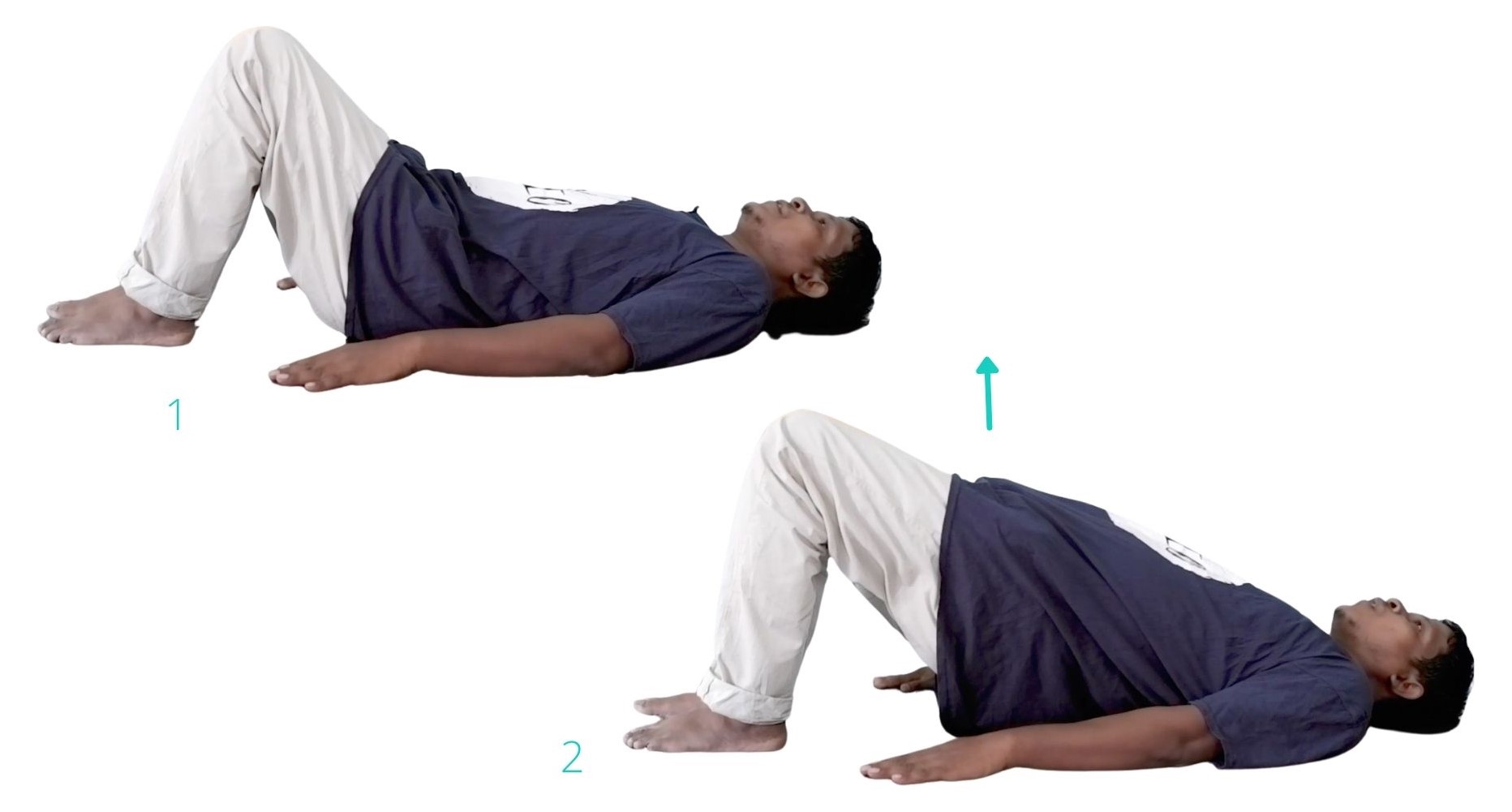
Image: physiosunit.com
Diagnosis of Posterior Disc Bulge: Unraveling the Cause
If you experience any of the symptoms mentioned above, it’s crucial to seek medical attention. A healthcare professional can thoroughly evaluate your condition and determine the best course of action. Here’s how a posterior disc bulge is typically diagnosed:
- Physical examination: Your doctor will examine your spine, check your reflexes, and assess your range of motion.
- Neurological examination: Your doctor may also test your reflexes, sensation, and muscle strength to assess the extent of nerve damage.
- Imaging tests: Imaging tests like X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans can provide detailed images of your spine and help identify a disc bulge, its size, and location.
Treatment for Posterior Disc Bulge: Finding Relief and Restoration
Depending on the severity of your pain and the nature of your disc bulge, your doctor will recommend the most appropriate treatment plan. Treatment options can range from conservative approaches to surgical interventions.
Conservative Treatment Options: Focusing on Recovery
- Rest: This is important in the early stages of a posterior disc bulge to allow the compressed nerve to heal. However, prolonged rest can lead to weakening muscles, so it’s crucial to find a balance between rest and gentle movement.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers: Pain medications like ibuprofen or naproxen can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Muscle relaxants: Muscle relaxants can help relieve muscle spasms and improve your comfort.
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy can help strengthen your muscles, improve flexibility, and teach you proper posture and body mechanics.
- Heat or ice therapy: Applying heat or ice to the affected area can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Epidural steroid injections: In some cases, your doctor may recommend epidural steroid injections to reduce inflammation and pressure around the compressed nerve.
Surgical Treatment Options: When Conservative Approaches Fall Short
In some cases, surgery may be necessary to relieve pressure on the nerve and prevent further damage. Surgical options include:
- Laminectomy: This procedure involves removing a portion of the bone (lamina) that covers the spinal canal to create more space for the nerve root.
- Discectomy: This procedure involves removing the compressed or herniated portion of the disc.
- Fusion: This procedure involves joining two or more vertebrae together to stabilize the spine and reduce motion in the affected area.
Living with a Posterior Disc Bulge: Empowering Yourself for Long-Term Health
Living with a posterior disc bulge requires a proactive approach to managing your symptoms and preventing further complications. Here are some crucial steps you can take:
- Maintain a healthy weight: Excess weight adds strain to your spine, so maintaining a healthy weight is essential to prevent further disc degeneration.
- Exercise regularly: Regular exercise, especially strengthening exercises for your back muscles, can help support your spine and reduce the risk of disc bulges.
- Practice good posture: Avoid slouching or sitting for long periods without breaks. Standing and sitting with good posture can reduce stress on your spine.
- Avoid heavy lifting: If your job or daily activities involve heavy lifting, try to minimize these activities or use proper lifting techniques.
- Limit twisting and bending: These movements can put strain on your spine, so try to find alternate ways to complete tasks.
- Take breaks during the day: If you have a sedentary job, make sure to take regular breaks to stretch and move around.
Posterior Disc Bulge
https://youtube.com/watch?v=16zuihJ6WOk
In Conclusion: Living a Pain-Free Life
A posterior disc bulge can be a painful and debilitating condition, but understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options empowers you to actively manage your health. By seeking medical attention, following your doctor’s recommendations, and practicing healthy habits, you can reduce your pain and minimize the impact of a posterior disc bulge on your life.
Remember that you are not alone in this journey. Many people experience disc bulges, and with the right knowledge and strategies, you can navigate this condition and achieve a fulfilling life.



/GettyImages-173599369-58ad68f83df78c345b829dfc.jpg?w=740&resize=740,414&ssl=1)


