Imagine this: you’re a small business owner, diligently tracking every expense and income. You’ve just paid your employees, but something doesn’t feel quite right. You know there’s a specific way to record these transactions in your accounting books, but you can’t quite recall the details. This is where understanding the art of 13-8 journalizing payroll transactions comes into play.
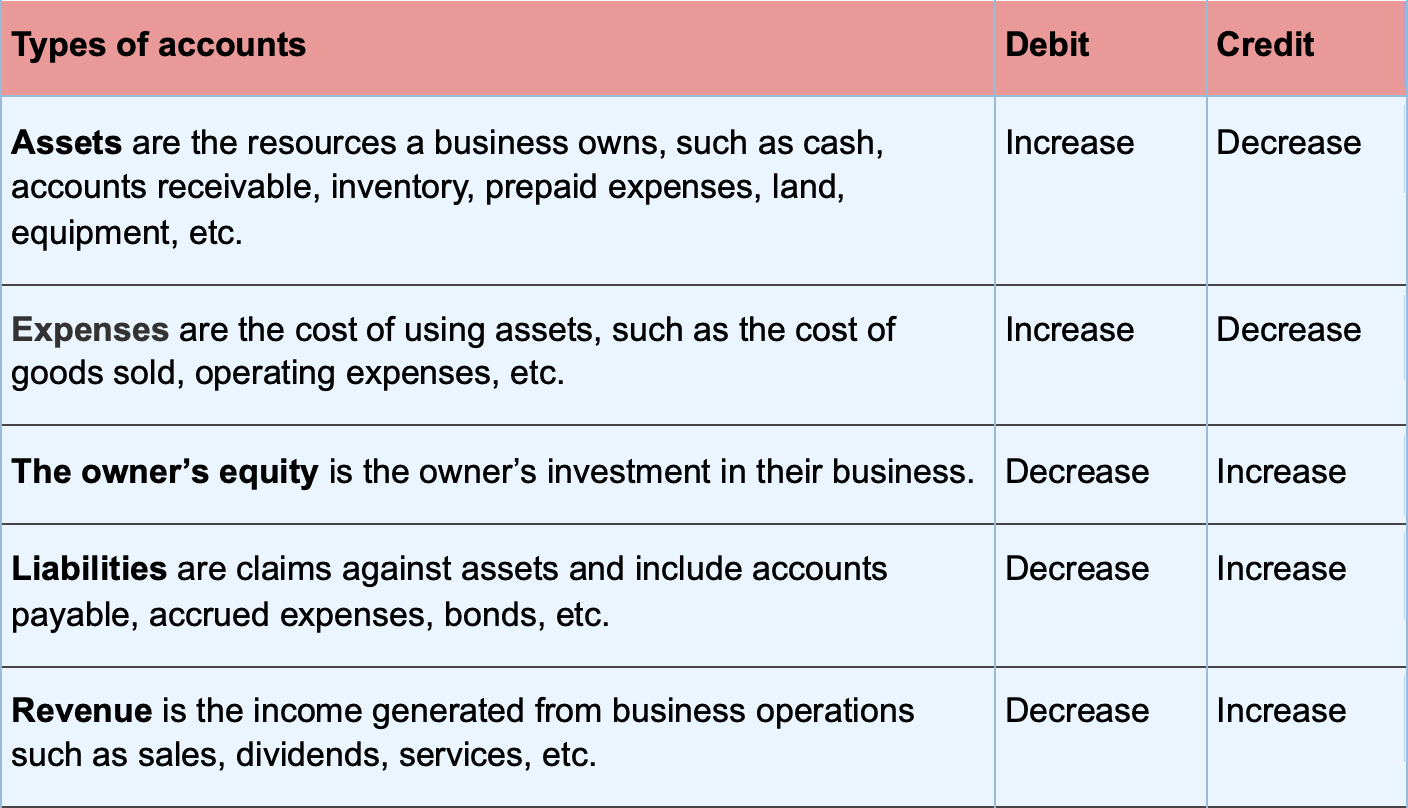
Image: waylonfersstein.blogspot.com
This seemingly complex process is the cornerstone of accurate financial reporting, ensuring your company’s financial health. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll demystify 13-8 journalizing, unraveling the intricacies of payroll transactions and empowering you with the knowledge to handle them confidently. Whether you’re a seasoned entrepreneur or just starting your business journey, this guide will provide you with the clarity you need.
What are 13-8 Journalizing Payroll Transactions?
Journalizing payroll transactions using the 13-8 method refers to a specific format used for recording employee wages and related payroll expenses in accounting ledgers. The term “13-8” originated from a time when payroll entries were made on pre-printed forms, with a specific layout for each payroll transaction. Although modern accounting software has largely replaced these forms, the essence of the process remains the same.
Understanding the Fundamentals
At its heart, the 13-8 method uses a double-entry bookkeeping approach, meaning every transaction affects at least two accounts, ensuring the accounting equation remains balanced. Here’s a breakdown of the key accounts involved in a typical 13-8 journal entry:
- Wages Expense: Represents the amount paid to employees for their services.
- Payroll Taxes: Covers various taxes withheld from employee wages, such as Social Security, Medicare, and federal income tax.
- Employee Withholdings: Reflects the amount withheld from employee wages that is payable to government agencies.
- Cash (or Bank): Shows the actual amount of cash paid out to employees.
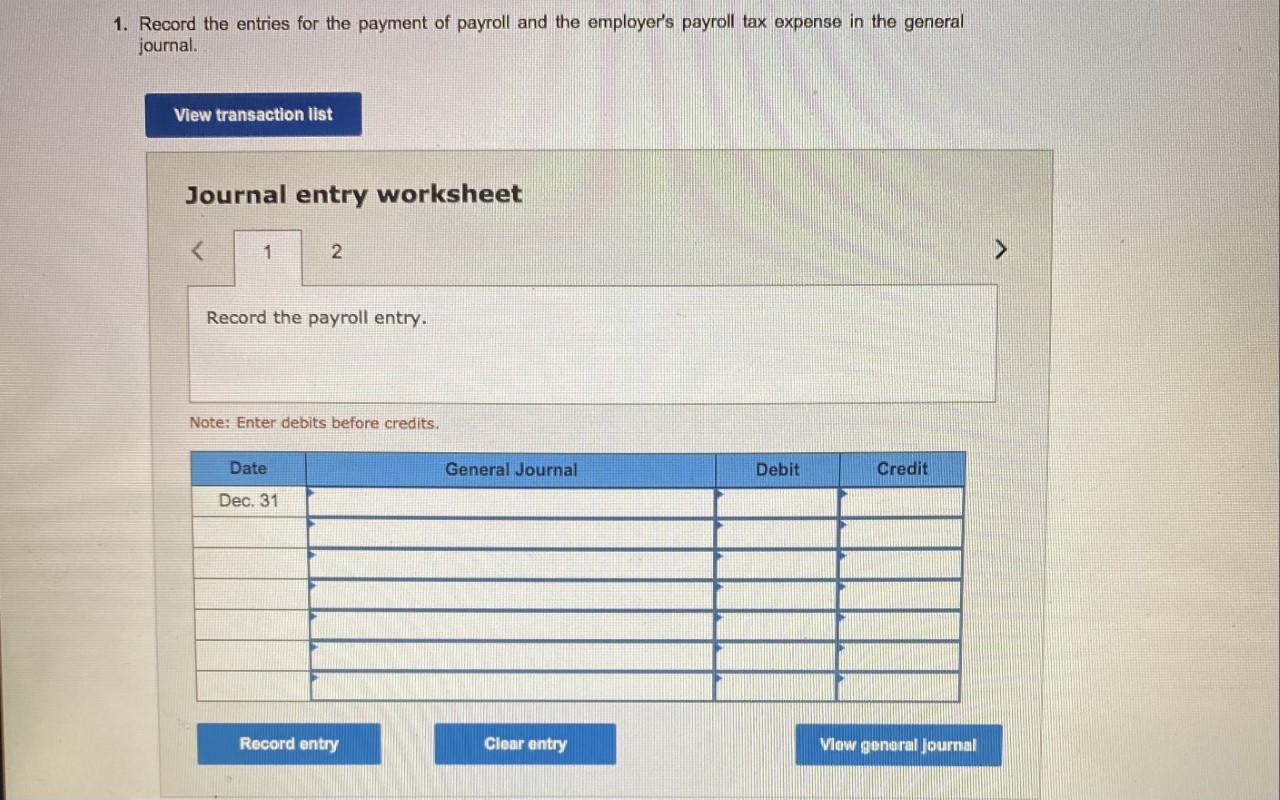
Image: www.chegg.com
13-8 Journalizing Payroll Transactions
Decoding the 13-8 Journalizing Process
Let’s dive into a practical example to illustrate the 13-8 method:
Scenario
A company pays its employees every Friday. This week, they had total wages of $10,000. From this amount, $1,200 was withheld for federal income tax, $750 for Social Security, and $175 for Medicare. The net wages paid to employees were $8,850.
Journal Entry
| Account | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Wages Expense | $10,000 | |
| Payroll Taxes | $2,125 | |
| Employee Withholdings | $1,200 | |
| Cash (or Bank) | $8,850 |
Explanation
- Wages Expense: This account is debited for $10,000 to reflect the total amount of wages paid to employees.
- Payroll Taxes: This account is credited for $2,125 ($750 for Social Security + $175 for Medicare). These are considered liabilities to the company because they represent taxes withheld from employee wages that are owed to the government.
- Employee Withholdings: This account is credited for $1,200, representing the federal income tax withheld from employee wages, which is also considered a liability.
- Cash (or Bank): This account is credited for $8,850, representing the net amount of cash paid to employees after deductions.
Why is 13-8 Journalizing Important?
Accurate recording of payroll transactions using the 13-8 method is crucial for several reasons:
- Compliance: Ensuring proper tax reporting and compliance with relevant regulations.
- Financials: Providing a clear and accurate picture of the company’s financial performance.
- Decision-making: Supporting sound business decisions based on reliable financial data.
- Auditing: Facilitating seamless audits by external auditors.
The 13-8 Method in Modern Accounting Software
While the traditional 13-8 method might seem cumbersome with its detailed breakdown, modern accounting software simplifies this process significantly. These programs automate payroll calculations, generate journal entries automatically, and provide seamless integration with payroll service providers.
Streamlining The Process
Think of accounting software as your personal assistant for payroll management. Here’s how it enhances your 13-8 journalizing workflow:
- Automatic Calculations: Software calculates employee wages, deductions, and taxes, reducing the risk of human error.
- Automated Journal Entries: Software automatically generates the journal entries based on the payroll data, eliminating the need for manual coding.
- Report Generation: Provides comprehensive reports for different payroll periods, including breakdowns of wages, deductions, and taxes paid.
Navigating the 13-8 Method: Tips for Success
- Choose the Right Accounting Software: Select software that integrates seamlessly with your payroll system and offers robust reporting features.
- Understand Your Payroll Regulations: Stay up-to-date with federal and state tax regulations to ensure compliance.
- Maintain Detailed Records: Keep accurate records of employee hours, pay rates, and deductions for accurate journalizing.
- Reconcile Your Accounts Regularly: Regularly compare your accounting records to your payroll system to identify any discrepancies.
Final Thoughts: Empowering You with Knowledge
13-8 journalizing payroll transactions might initially appear complex, but with the right understanding and tools, it’s a straightforward process that guarantees accurate financial reporting. By implementing the tips provided in this guide, you can confidently manage your payroll transactions and maintain a healthy financial foundation for your business. Remember, accurate records are the bedrock of informed decision-making and a successful business journey.



/GettyImages-173599369-58ad68f83df78c345b829dfc.jpg?w=740&resize=740,414&ssl=1)


